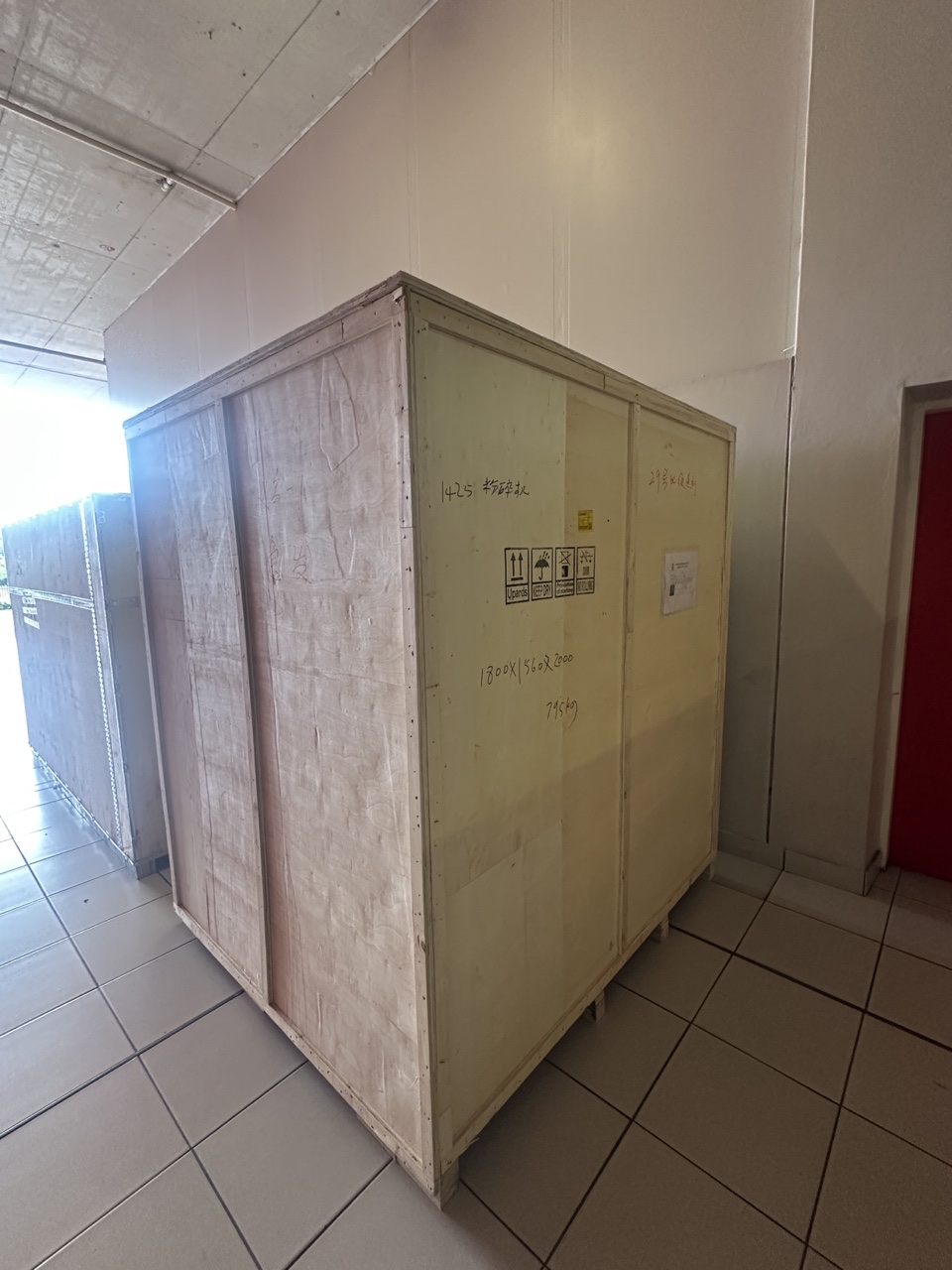
B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
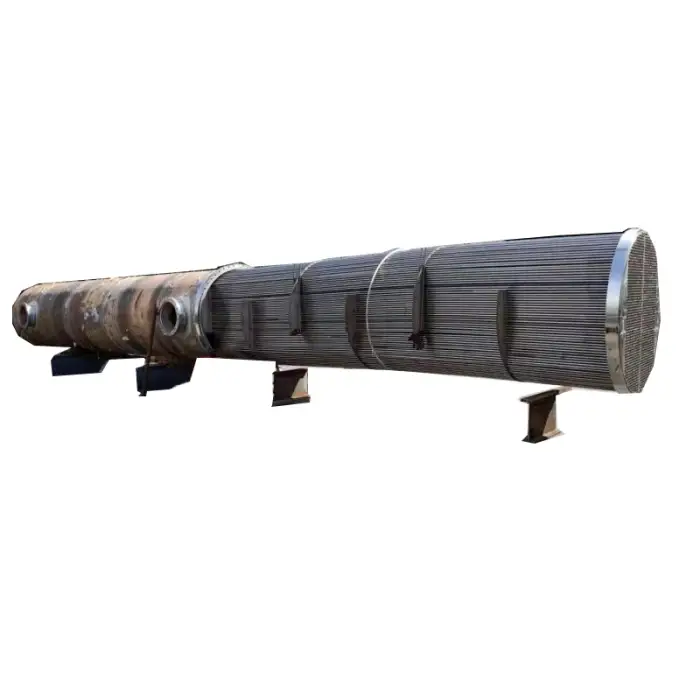
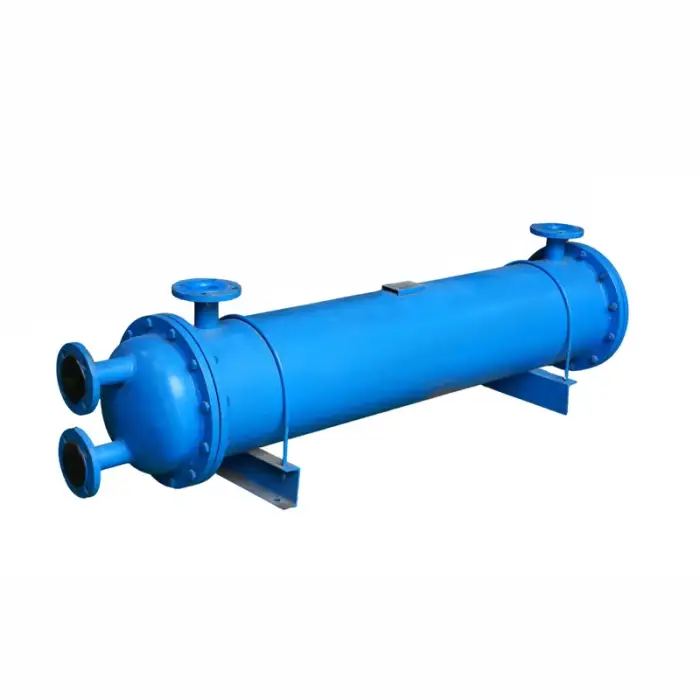
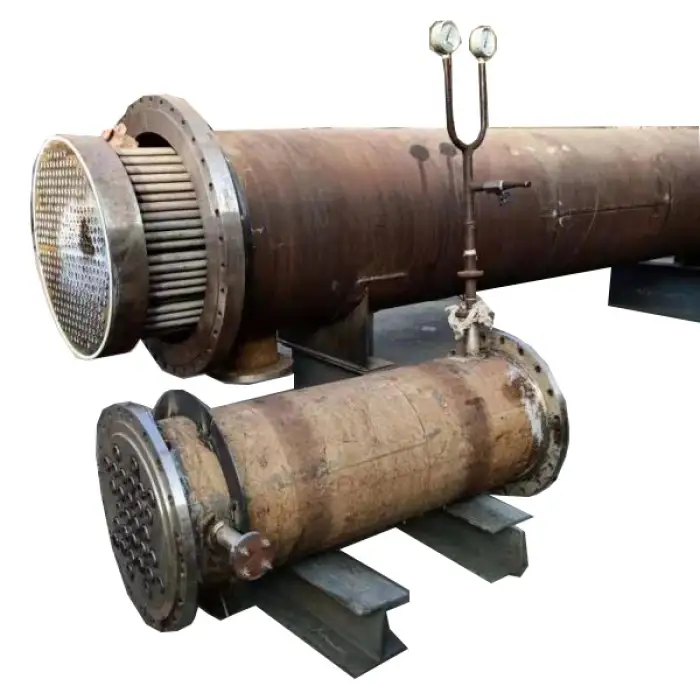
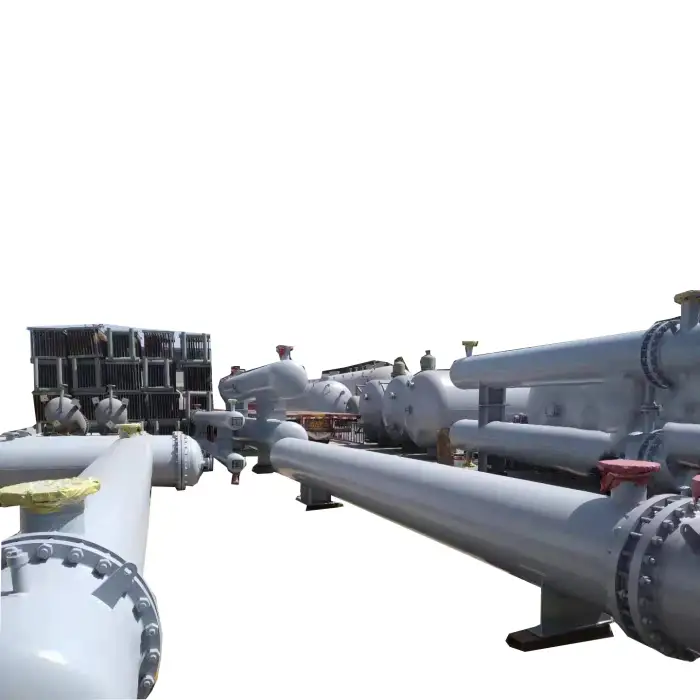
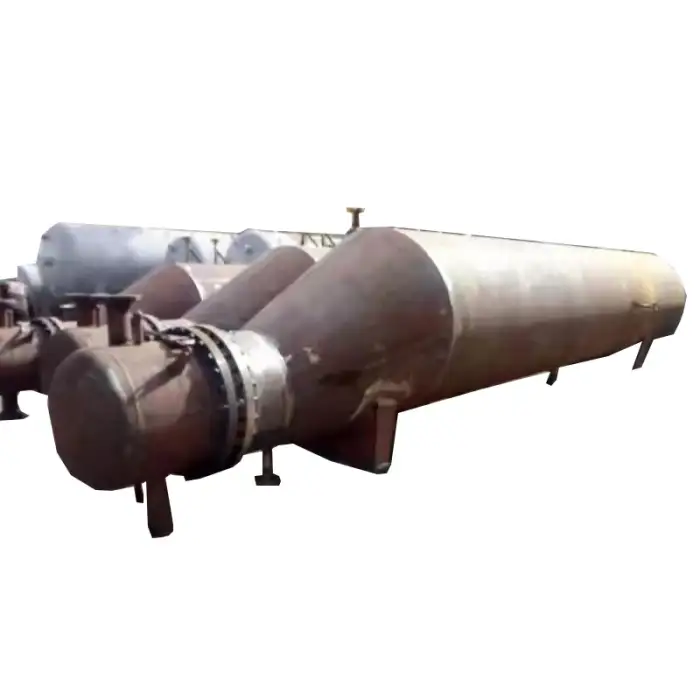
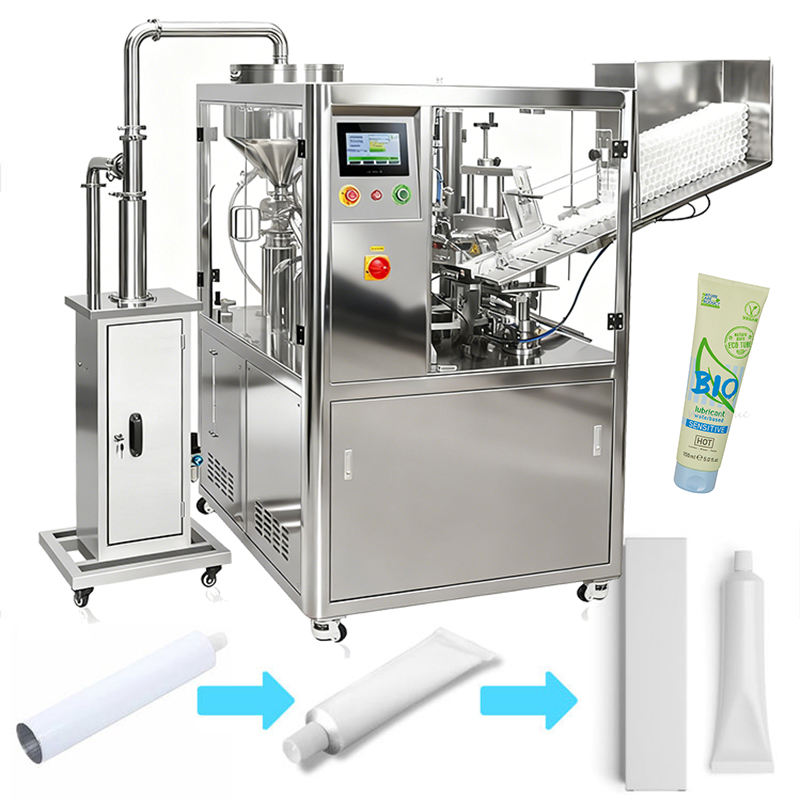
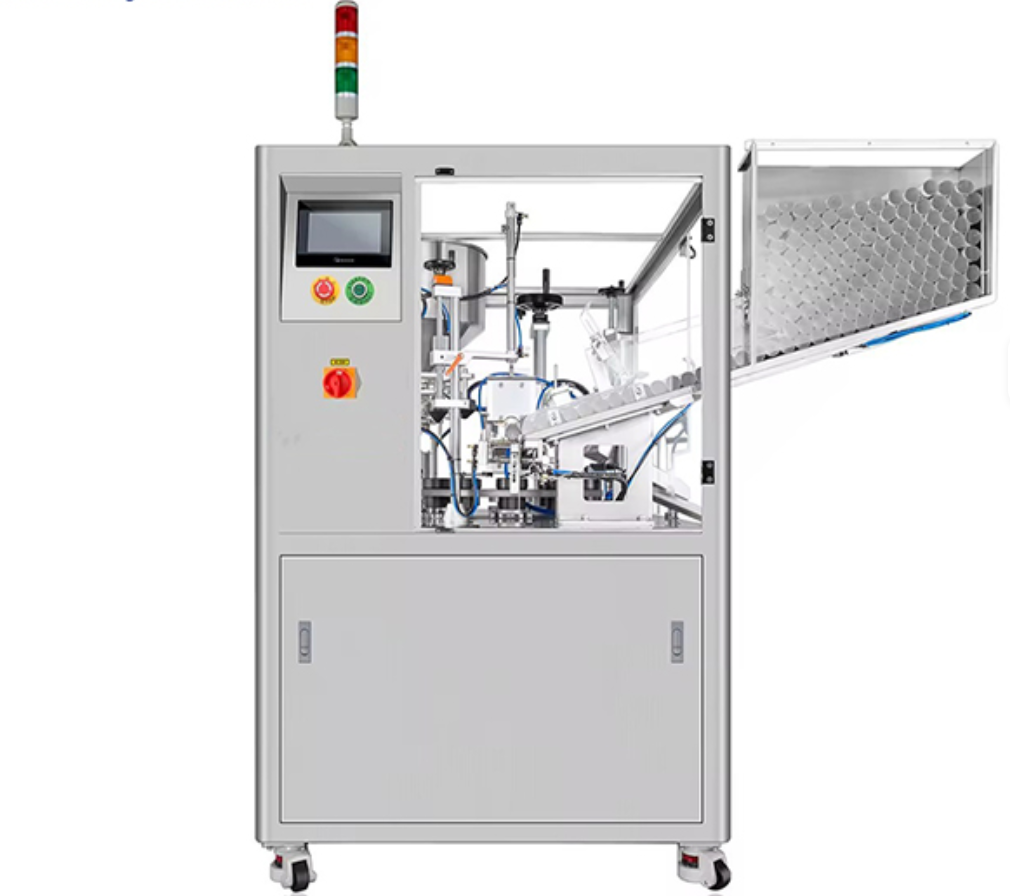
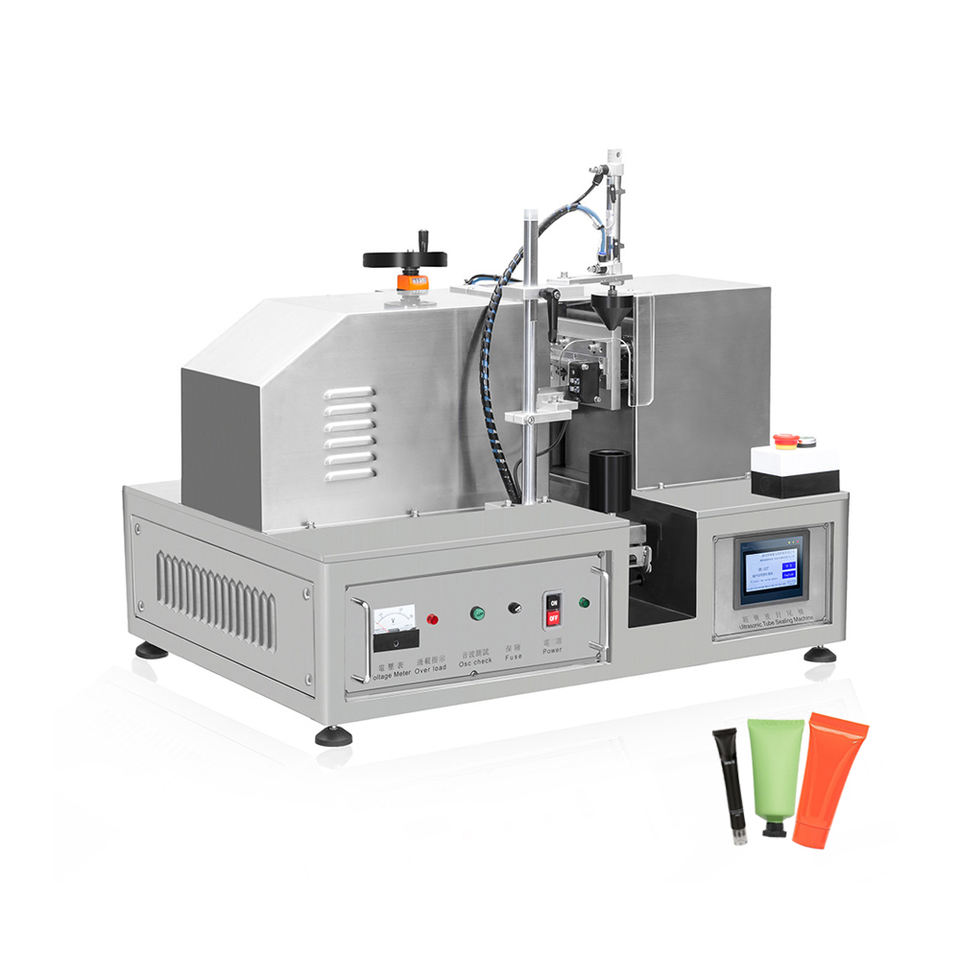
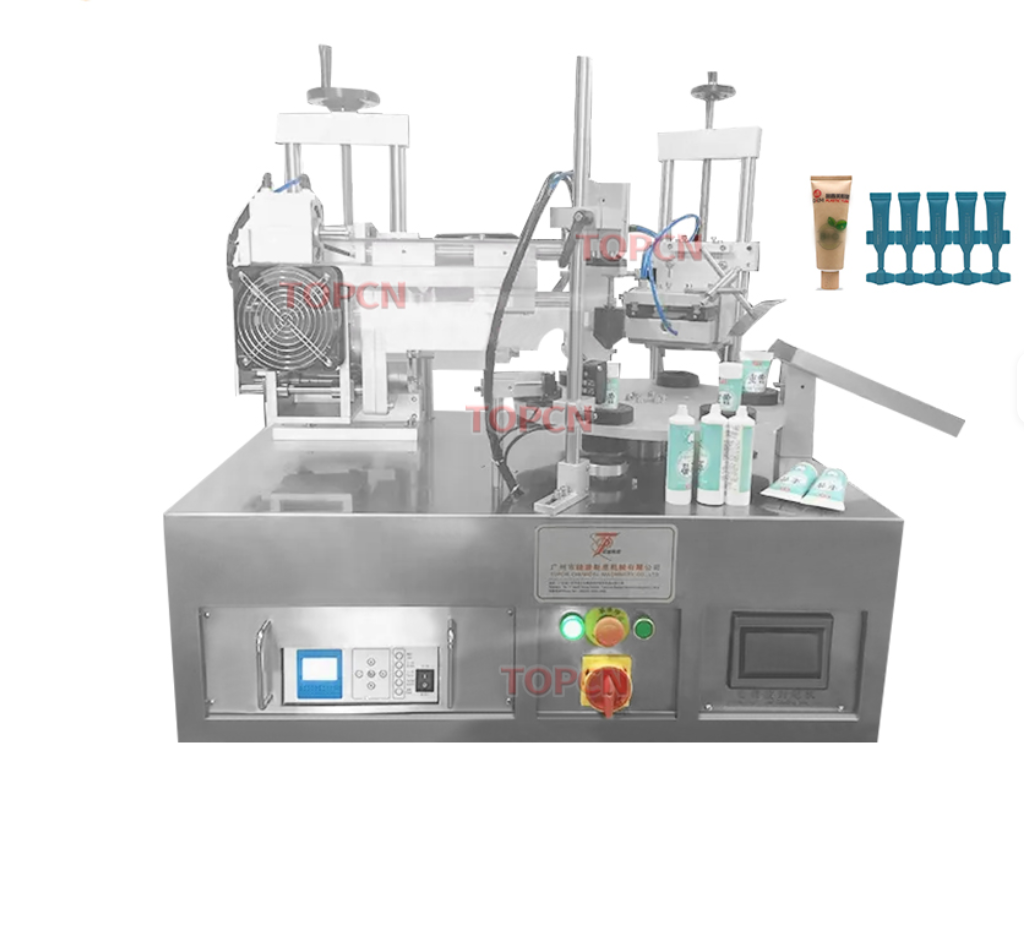
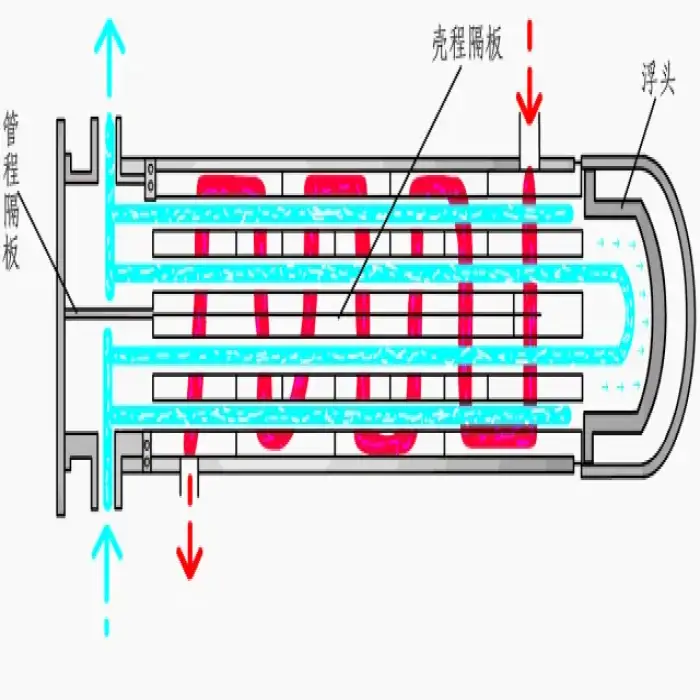
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Tubular Heat Exchanger
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Industrial Machinery
- SKU : 1600259512109

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 28 Apr, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is a shell and tube heat exchanger?
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger that consists of a series of tubes, one set carrying the hot fluid and the other carrying the cold fluid, allowing for efficient heat transfer between the two fluids.
2. What are the main applications of shell and tube heat exchangers?
Shell and tube heat exchangers are commonly used in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and HVAC systems, for heating, cooling, and condensing applications.
3. How does a shell and tube heat exchanger work?
The heat exchanger works by allowing one fluid to flow through the tubes while another fluid flows around the tubes within the shell. Heat is transferred from the hot fluid to the cold fluid through the tube walls.
4. What materials are used in the construction of shell and tube heat exchangers?
Shell and tube heat exchangers can be made from a variety of materials, including stainless steel, carbon steel, and various alloys, depending on the application and the fluids being processed.
5. What factors should be considered when selecting a shell and tube heat exchanger?
Key factors include the type of fluids being used, temperature and pressure conditions, required heat transfer efficiency, and space constraints, as well as maintenance and cleaning requirements.
6. What is the typical maintenance for shell and tube heat exchangers?
Regular maintenance includes inspecting for leaks, checking for fouling or scaling, cleaning the tubes, and ensuring that all seals and gaskets are in good condition to maintain efficiency.
7. Can shell and tube heat exchangers handle high-pressure applications?
Yes, shell and tube heat exchangers are designed to withstand high-pressure applications, making them suitable for various industrial processes.
8. What is the difference between a shell and tube heat exchanger and a plate heat exchanger?
The main difference lies in their design; shell and tube heat exchangers use tubes to transfer heat, while plate heat exchangers use thin plates. Shell and tube units are typically better for high-pressure applications, while plate units are more compact and efficient for smaller flows.
9. How do I determine the appropriate size for a shell and tube heat exchanger?
Sizing is determined based on the required heat transfer rate, flow rates of the fluids, temperature differences, and process conditions. It's best to consult with a heat exchanger manufacturer or engineer for precise calculations.
10. Are shell and tube heat exchangers suitable for corrosive fluids?
Yes, they can be designed to handle corrosive fluids by using suitable materials like titanium or special alloys to prevent corrosion and ensure longevity.
11. What are the advantages of using shell and tube heat exchangers?
Advantages include high efficiency, durability, ease of maintenance, the ability to handle large temperature differences, and versatility in design.
12. What is the typical lifespan of a shell and tube heat exchanger?
The lifespan can vary widely based on the operating conditions, materials used, and maintenance practices, but generally, they can last for 10 to 30 years or more with proper care.
13. Can shell and tube heat exchangers be used for both heating and cooling?
Yes, shell and tube heat exchangers can be designed for both heating and cooling applications, making them versatile in various industrial processes.
14. What is fouling, and how does it affect shell and tube heat exchangers?
Fouling refers to the accumulation of unwanted material on the heat transfer surfaces, which can reduce efficiency and heat transfer rates. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to minimize fouling.
15. Is it possible to customize shell and tube heat exchangers?
Yes, they can be customized in terms of size, material, and design features to meet specific application requirements.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories
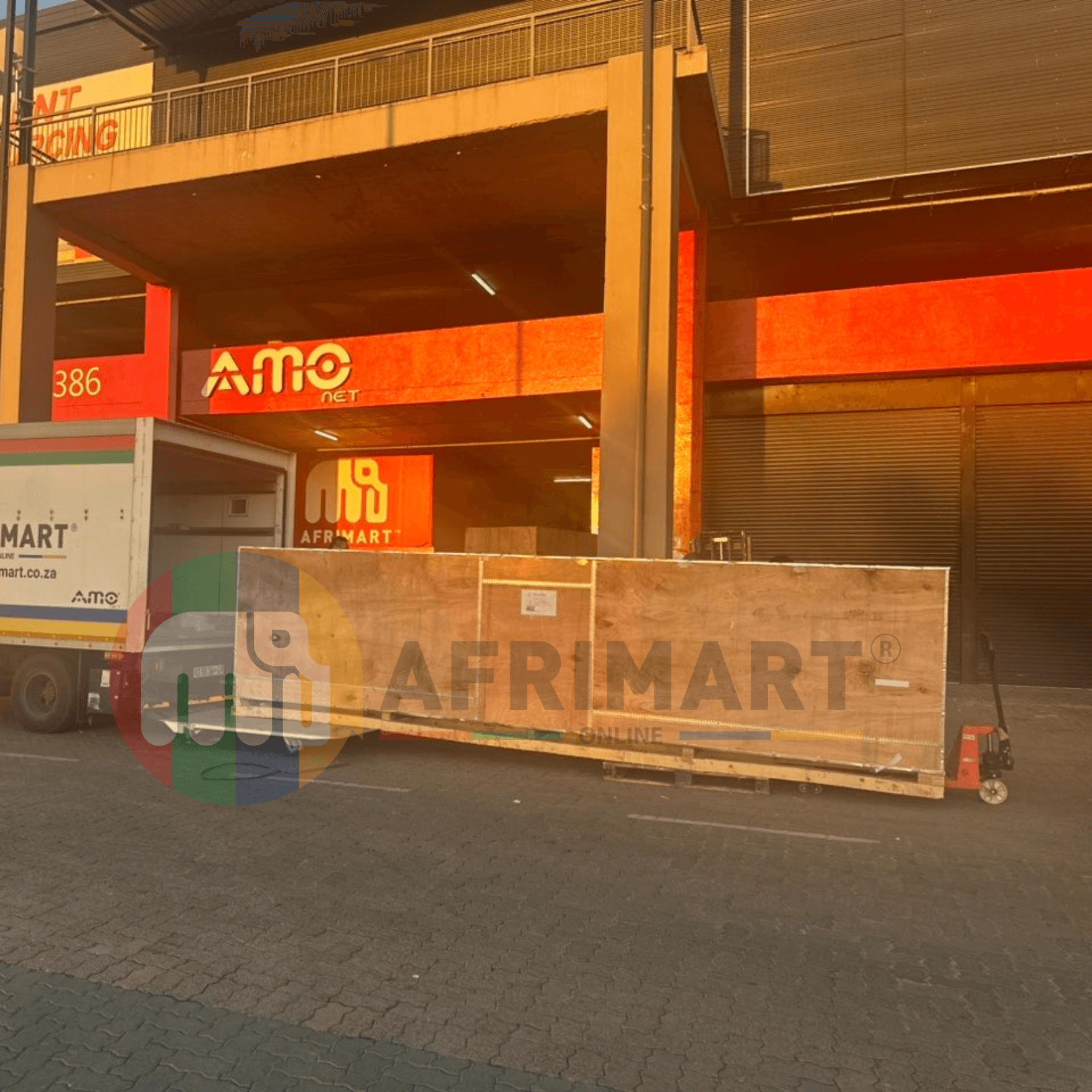

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment
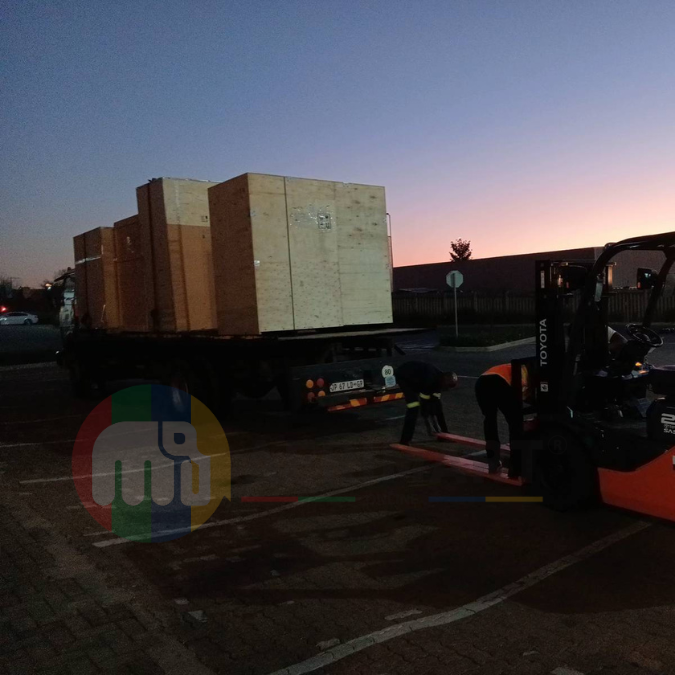

Mining Equipments
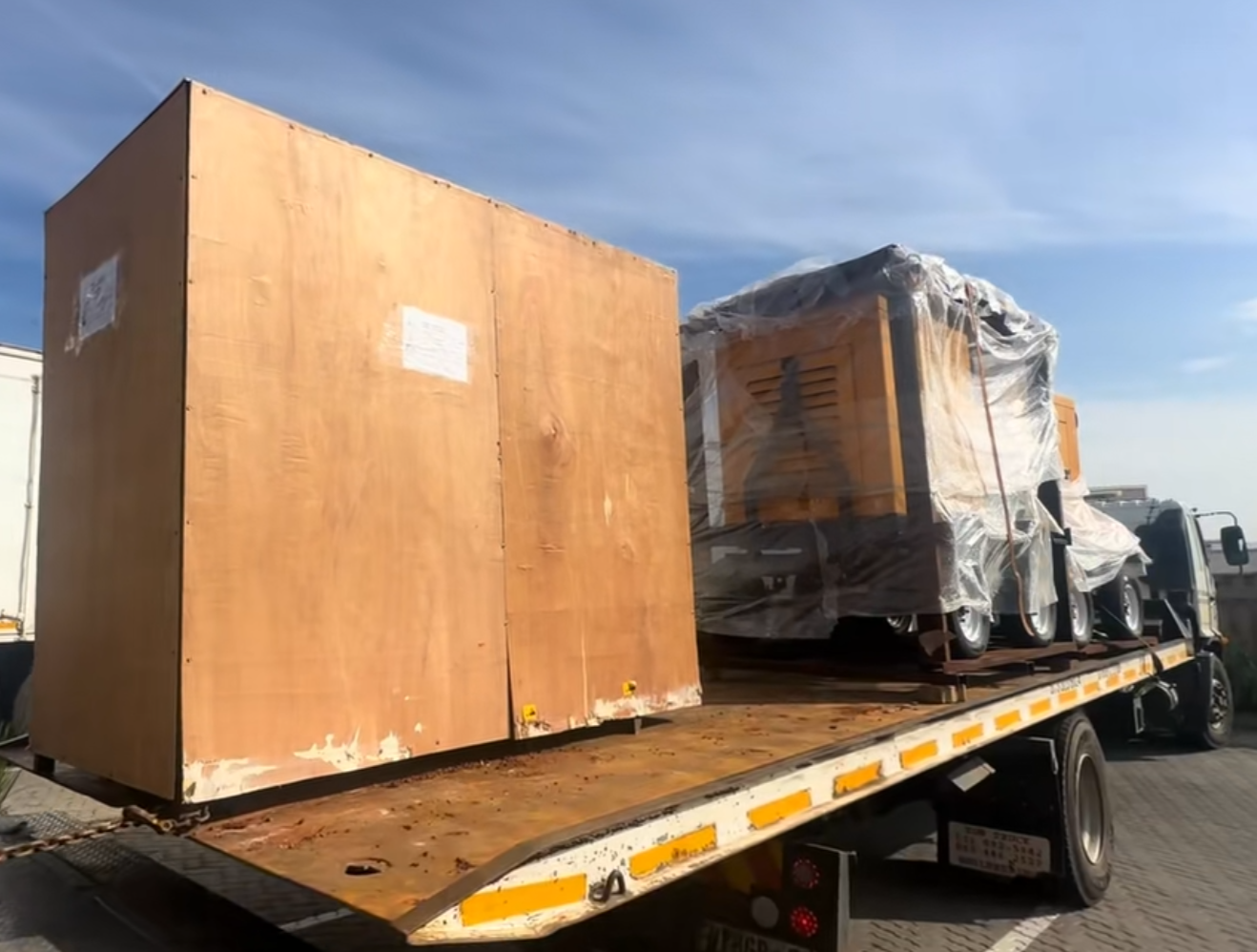

Food Processing Machine
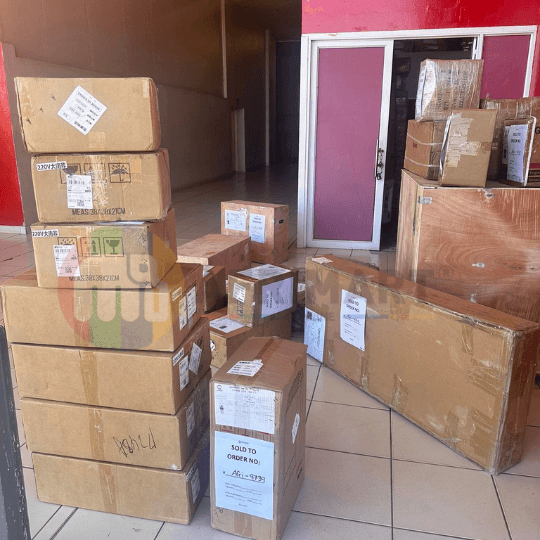

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading