B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
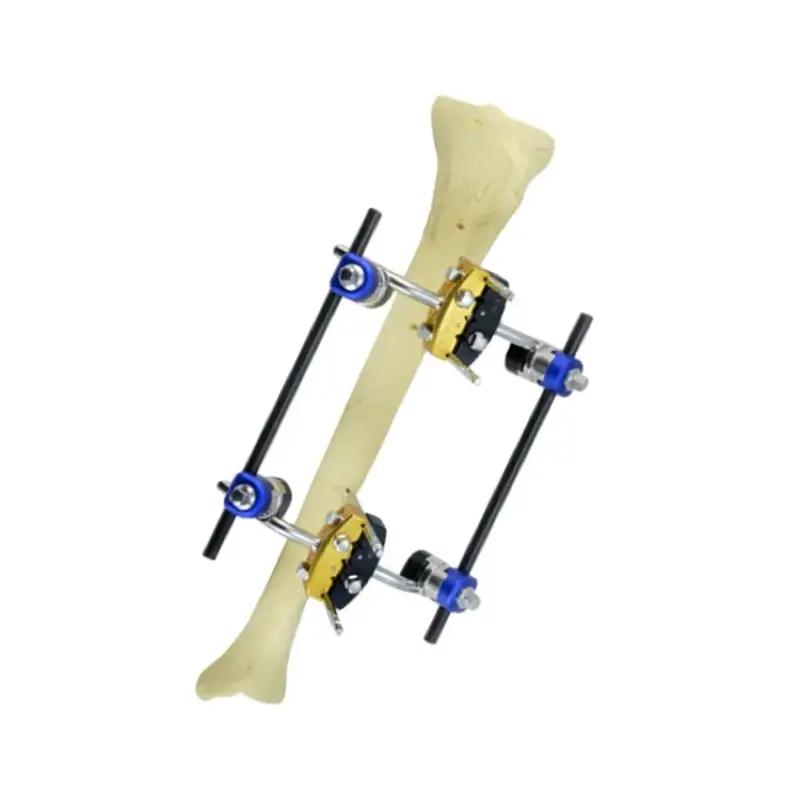
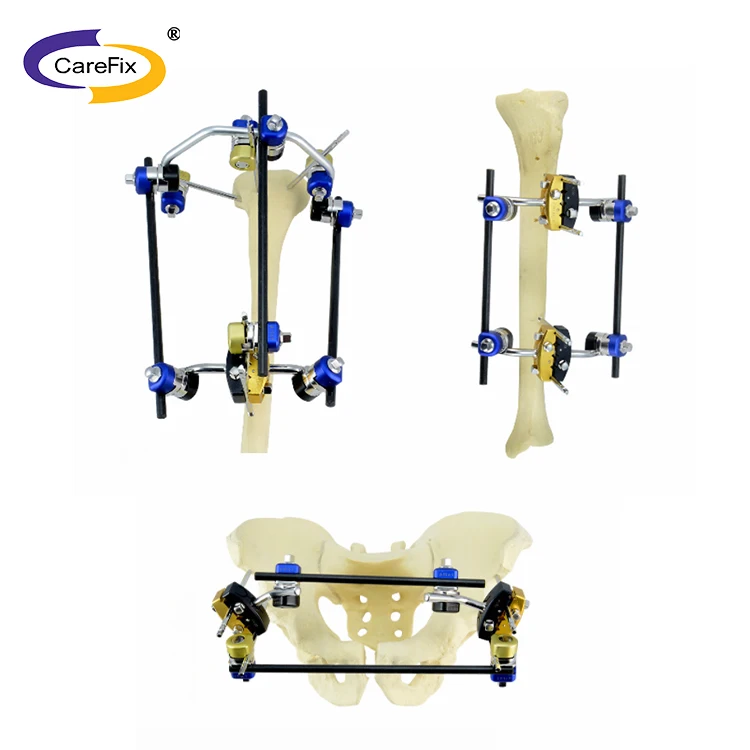
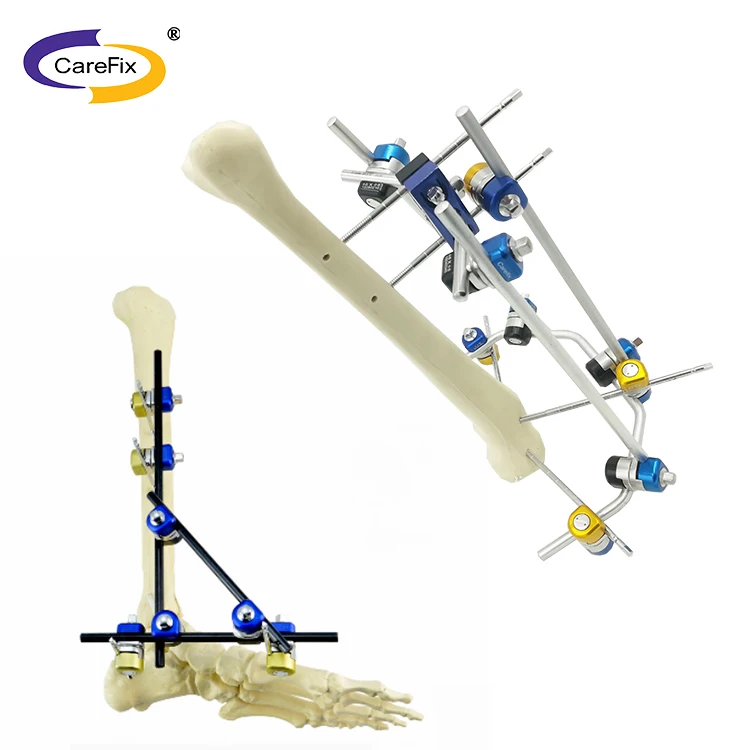
Combined External Fixator For Orthopedic Surgery
- Section : Medical Supplies
- Category : Bone Surgical Instruments
- SKU : 1600259793427

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 31 Jan, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is a Combined External Fixator for Orthopedic Surgery?
A Combined External Fixator is a modular surgical device used to stabilize and align fractured bones from outside the body. It provides temporary or definitive support for fracture management and joint stabilization during surgery and the healing period.
2. What clinical indications is this fixator used for?
It is used for management of complex or comminuted fractures, open fractures, limb lengthening, peri-articular fractures, and situations where internal fixation is not feasible or advisable. Indications should be determined by a qualified orthopedic surgeon.
3. What materials is the fixator made from?
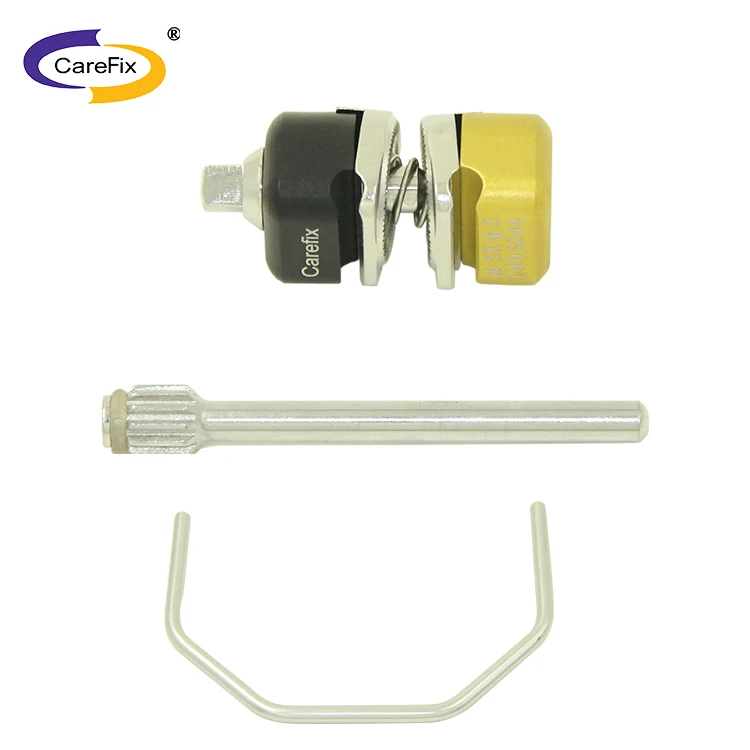
Components are generally manufactured from high-quality medical-grade materials such as stainless steel, titanium alloys, and (for some rod components) carbon fiber. Exact materials vary by model—refer to the product specification sheet for details.
4. What does 'Class III Instrument' mean?
'Class III' indicates the device is designed to meet stringent medical-device safety and performance standards. In some regulatory systems (e.g., FDA), Class III denotes higher-risk devices subject to greater premarket controls. Confirm the device's regulatory approvals and certifications for your region.
5. Is the fixator reusable or single-use?
This depends on the specific model and manufacturer labeling. Some external fixator systems are reusable after validated cleaning and sterilization; others or certain disposable components may be single-use. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions for use (IFU).
6. How is the device sterilized?
Sterilization methods depend on component materials. Many components are compatible with standard steam autoclave cycles (e.g., 121–134°C). Heat-sensitive parts may require low-temperature sterilization. Always use the sterilization parameters provided in the IFU.
7. Are the components compatible with medical imaging?
Metallic components will appear on X-ray and fluoroscopy; some systems include radiolucent rods or radiographic markers to aid imaging. Check the product spec for radiolucency and imaging guidance.
8. What sizes and configurations are available?
Combined external fixators are typically modular, offering a range of pin sizes, rod lengths, clamps, and ring options to accommodate different bones and fracture patterns. Refer to the manufacturer’s catalog for available sizes and configuration kits.
9. How is the fixator applied and who should perform the procedure?
Application requires an experienced orthopedic surgeon trained in external fixation techniques. The procedure includes pin/wire insertion, clamp/rod assembly, and alignment adjustments. Training and familiarity with the specific system are recommended.
10. What postoperative care and monitoring are required?
Postoperative care typically includes regular wound and pin-site care, monitoring for infection, periodic radiographic assessment of alignment and healing, and mechanical checks of the frame. Specific care protocols should follow institutional standards and surgeon instructions.
11. What are common risks or complications associated with external fixators?
Potential complications include pin-site infection, loosening of pins or clamps, neurovascular irritation, malalignment if not properly applied, and soft-tissue problems. Risks are minimized by proper surgical technique, device maintenance, and follow-up.
12. How should the device be inspected and maintained between uses?
Inspect for wear, corrosion, damaged threads, and integrity of locking mechanisms. Clean and lubricate as recommended by the manufacturer. Replace any components that show damage or out-of-tolerance wear before reuse.
13. Can this fixator be used with accessories from other manufacturers?
Some accessories may be interoperable if dimensions and thread types match, but cross-compatibility can vary and may compromise performance. Use manufacturer-approved accessories or verify compatibility before combining components.
14. What information is included in the product documentation?
Documentation typically includes indications, contraindications, warnings, component lists, assembly and application instructions, sterilization parameters, maintenance guidance, and regulatory certifications. Always review the Instructions for Use (IFU) before use.
15. How can I order the fixator or request customization and support?
Contact the manufacturer or authorized distributor for ordering, available kits, custom configurations, training, and technical support. Provide details on desired components, sizes, and any institutional purchasing requirements.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment
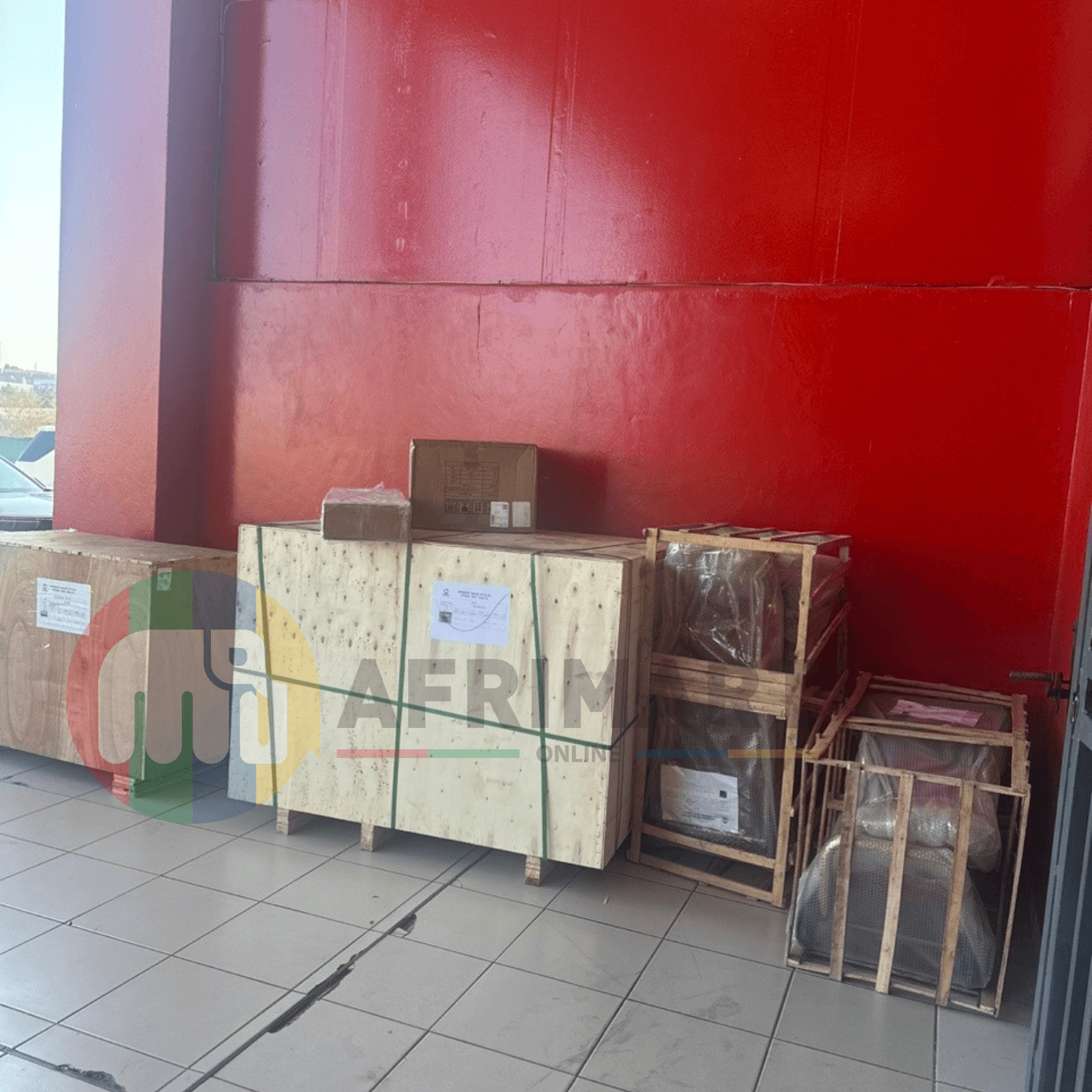

Packaging Machine and accessories
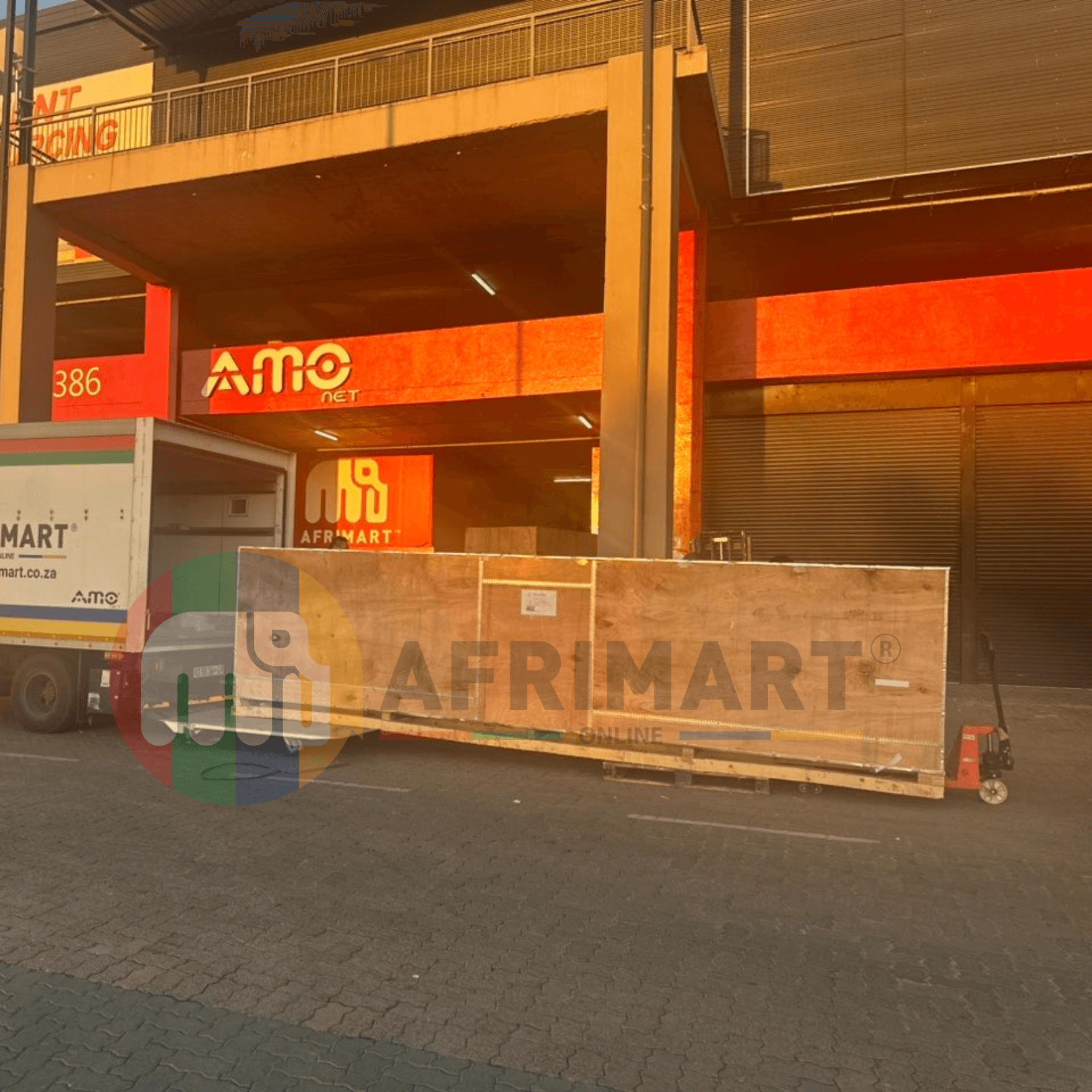

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment
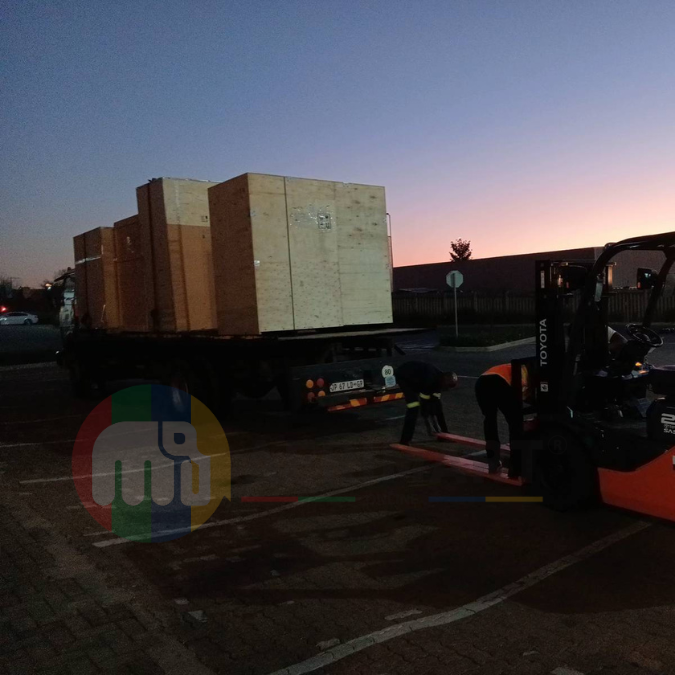

Mining Equipments
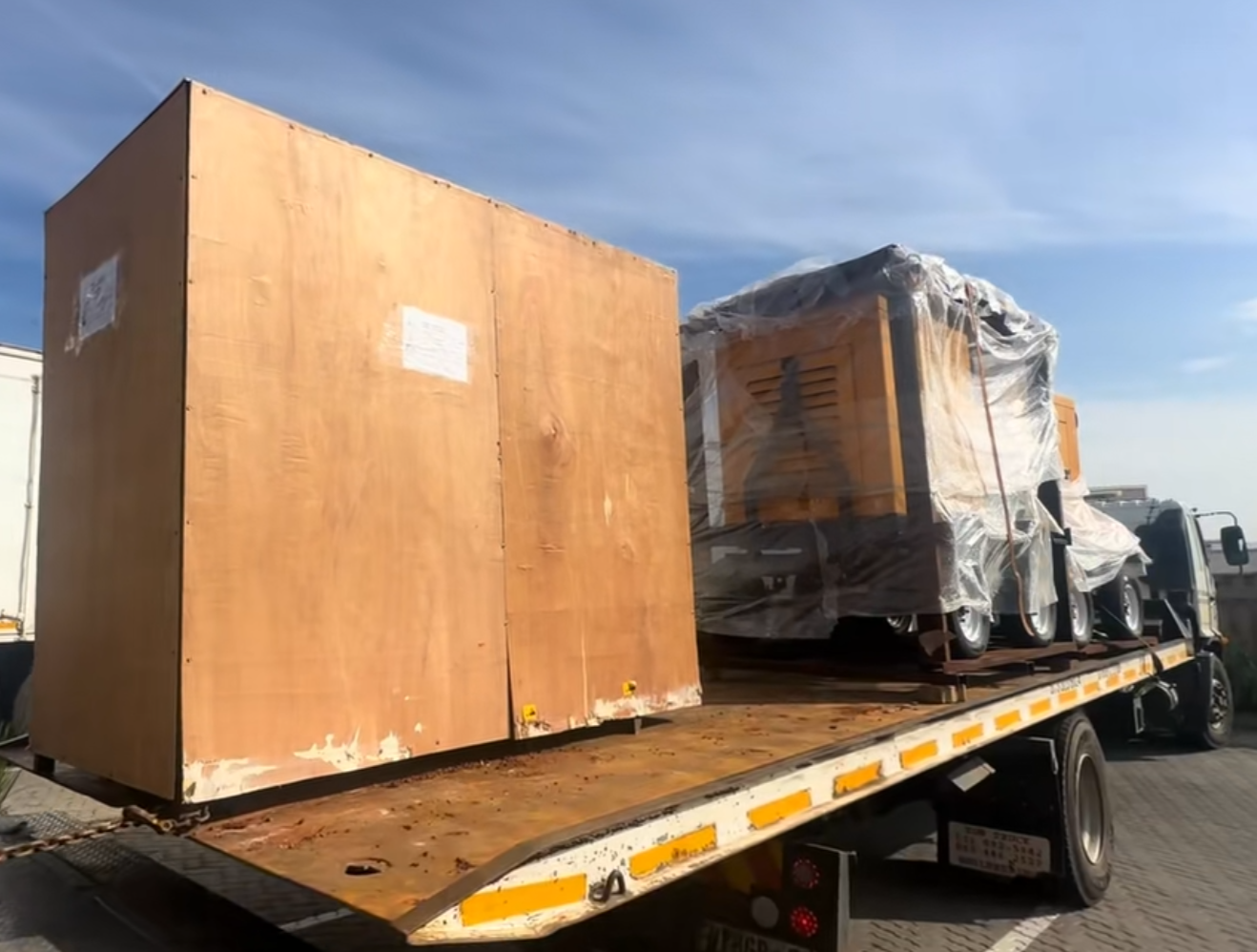

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

















