B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
Automatic Wall Cement Plastering Machine
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Construction Machinery
- SKU : 1601234564981

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 25 Apr, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is an Automatic Wall Cement Plastering Machine?
A mechanical system that mixes, pumps and sprays cement-based plaster onto vertical surfaces to automate manual plastering work, improving speed, consistency and finish quality.
2. How does the machine work?
Generally it feeds pre-mixed mortar into a pump, which forces the material through a hose to a spray nozzle; some models apply and level the plaster automatically while others require a trowel for finishing.
3. What materials can it handle?
Typically cement-sand mortars, lime-cement mixes and many gypsum or polymer-modified renders. Compatibility depends on particle size and mix viscosity—check the machine's specifications for max aggregate size and recommended mixes.
4. What plaster thickness and finish can I achieve?
Typical effective plaster thickness ranges from about 2–30 mm per pass depending on nozzle, pressure and model. Multiple passes can build greater thickness; finishing (skim/trowel) may be required for smooth or decorative surfaces.
5. How much area can it cover per hour (productivity)?
Productivity varies with material, thickness and operator skill. Typical rates are roughly 50–400 m²/hour. Lightweight skim coats reach higher rates; thick coarse renders are slower.
6. What power sources are available and what are the electrical requirements?
Machines are offered with electric motors (single‑phase or three‑phase) or diesel engines. Power requirements vary by model—small units may use 1–3 kW single‑phase, larger pumps 5–15 kW three‑phase or equivalent diesel power.
7. Does the unit include a mixer or do I need a separate mixer?
Many automatic plastering machines include an integrated mixer (paddle or twin‑shaft), but some compact units require a separate mixer. Confirm the model specification before purchase.
8. What surface preparation is required before using the machine?
Surfaces should be clean, free of loose material, properly wetted or primed (bond coat) where required, and any cracks or joints repaired. Proper scaffolding or access is also necessary for safe and even application.
9. How many operators are needed and is training required?
Most machines operate with 1–3 people: one feeding/mixing, one controlling the spray/nozzle and sometimes one finisher. Basic operator training on machine setup, mixing ratios, nozzle handling and safety is recommended and often provided by the supplier.
10. How long does setup and dismantling take?
Portable units can typically be set up in 15–60 minutes depending on site conditions and hose length. Larger trailer‑mounted systems or complex jobs may take longer. Routine pre-start checks are recommended.
11. What maintenance and cleaning are required?
Daily cleaning of hoses, pump and hopper is essential to prevent clogging and material cure. Regular inspection and replacement of wear parts (seals, valves, nozzles, hoses), lubrication of moving parts and periodic motor/engine service are required per the manufacturer's schedule.
12. Are spare parts and service available?
Yes—reputable manufacturers and dealers supply spare parts (wear rings, pistons, seals, nozzles, hoses) and service. Confirm local dealer support and spare parts availability before purchase to minimize downtime.
13. Is the machine portable and what are typical weights/dimensions?
Models range from compact wheeled units (roughly 100–400 kg) to larger trailer or truck‑mounted systems (500 kg to several tonnes). Choose based on site access, transport and project scale.
14. What safety features should I expect?
Look for emergency stop buttons, pressure relief valves, guards around moving parts, secure hose couplings and clear operating manuals. Operators should use PPE—eye/ear protection, gloves, respirators and safe handling for cementitious materials.
15. What about warranty, certifications and purchasing considerations?
Warranties typically range from 6–24 months depending on manufacturer and part. Check for quality certifications (CE, ISO) and ask for references, on‑site demonstrations, training packages and after‑sales support when evaluating suppliers.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories
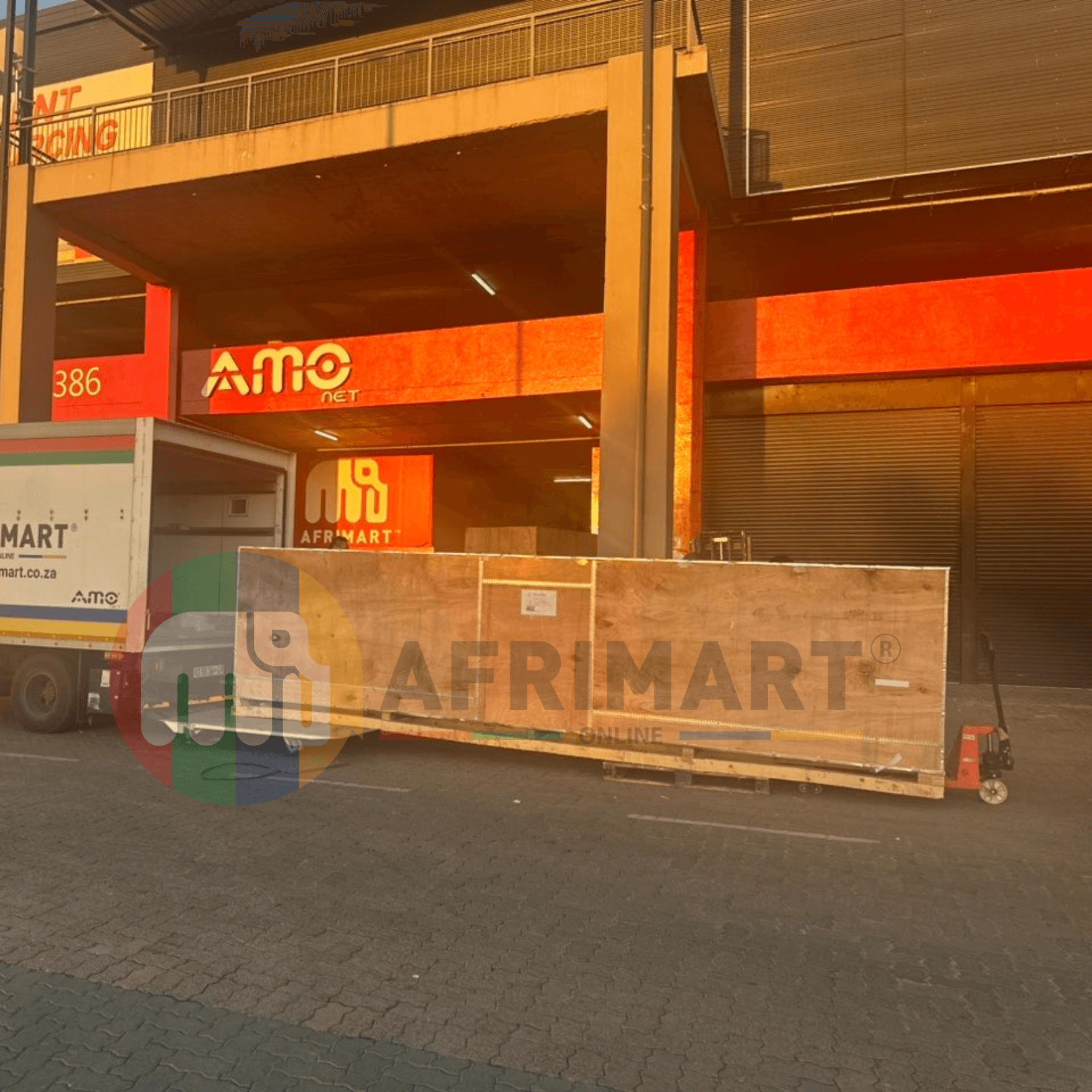

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment
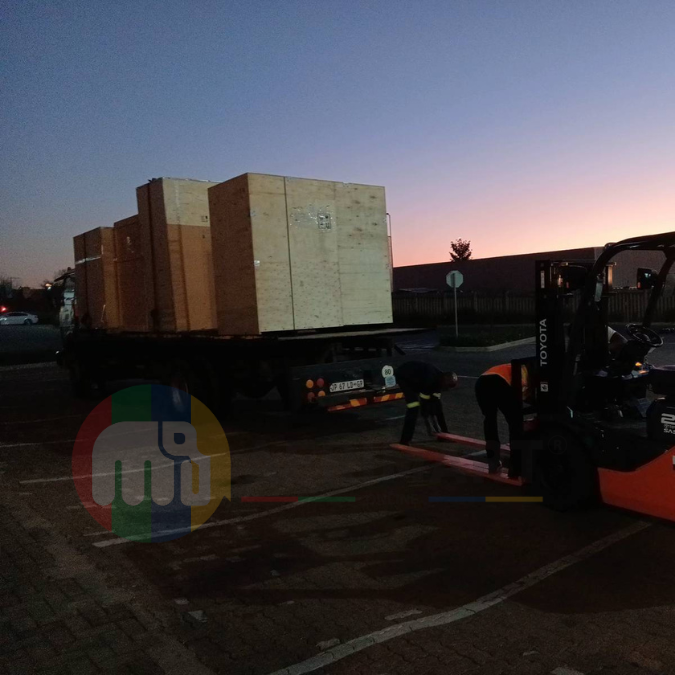

Mining Equipments
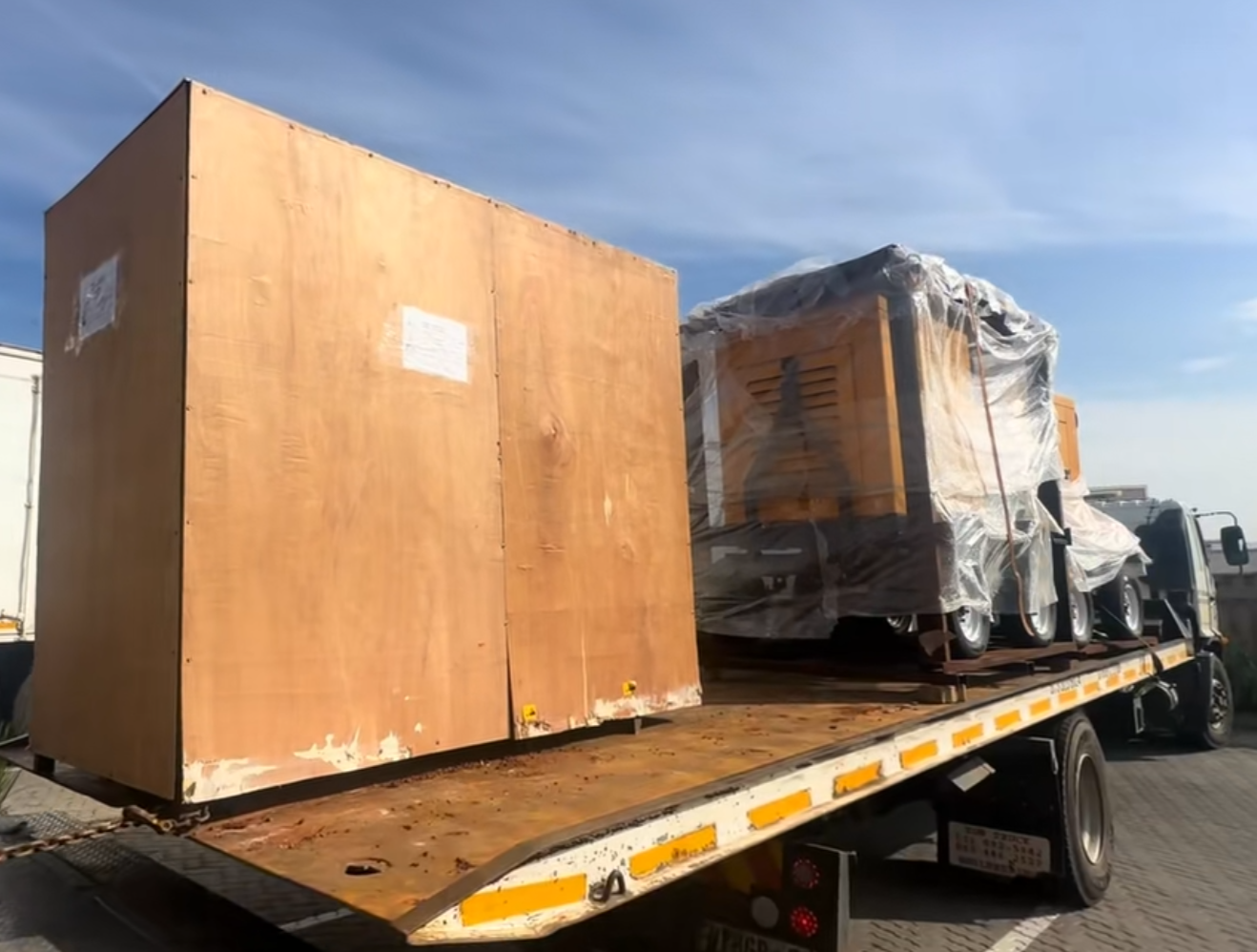

Food Processing Machine
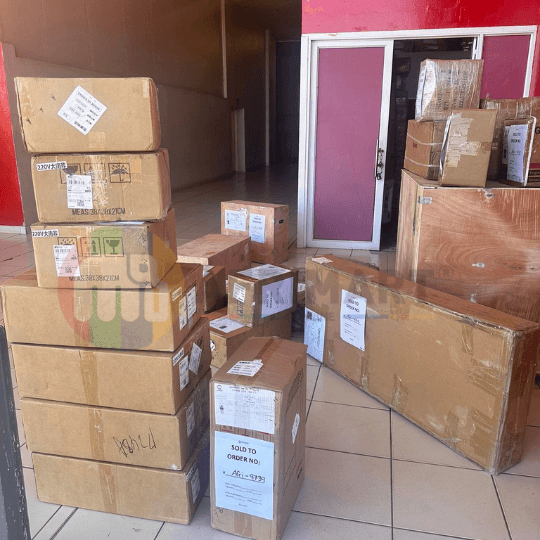

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading
















