B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
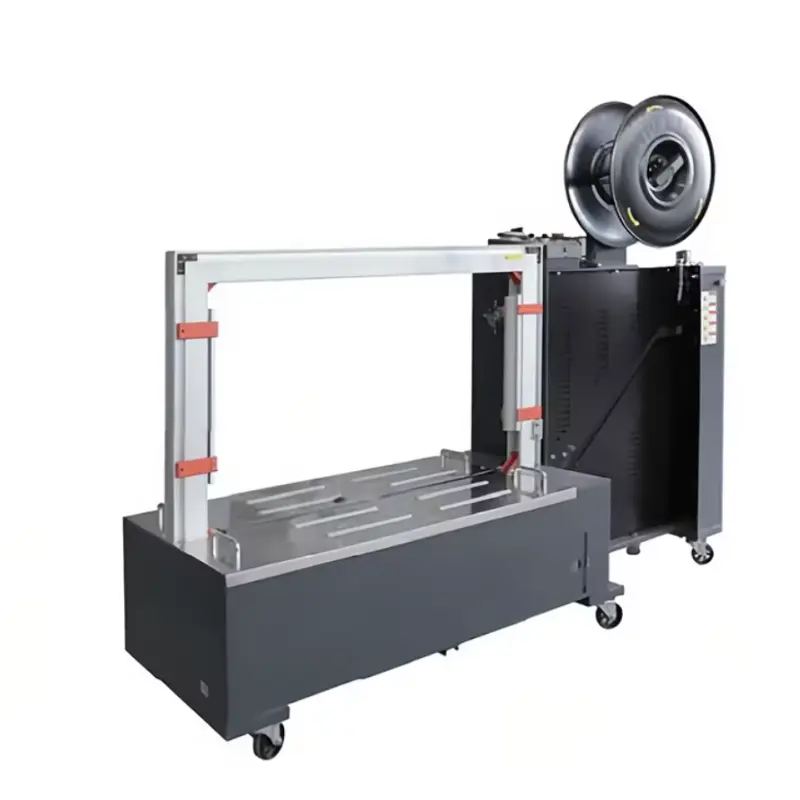
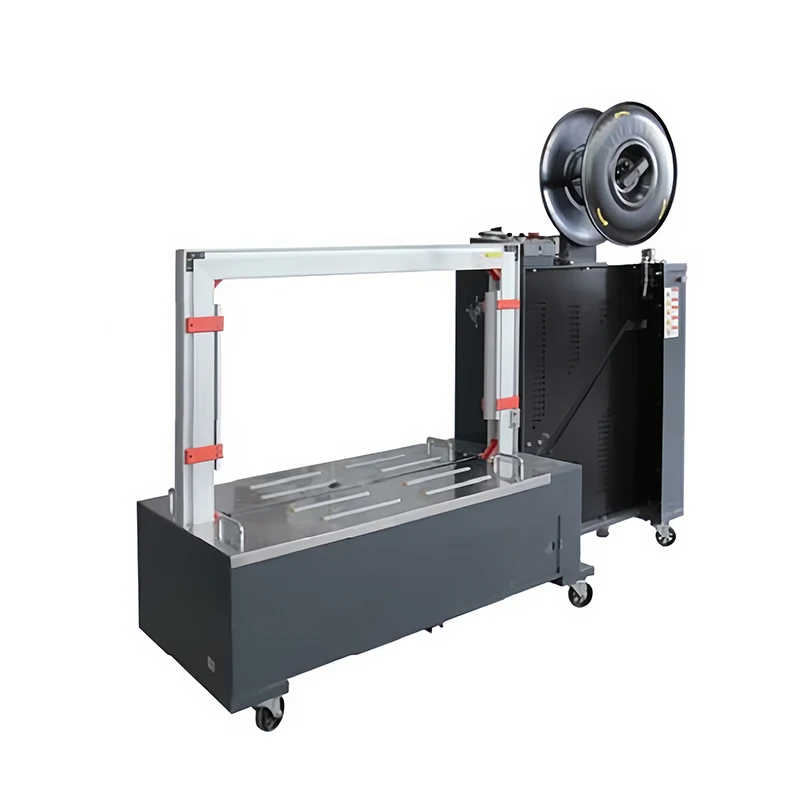
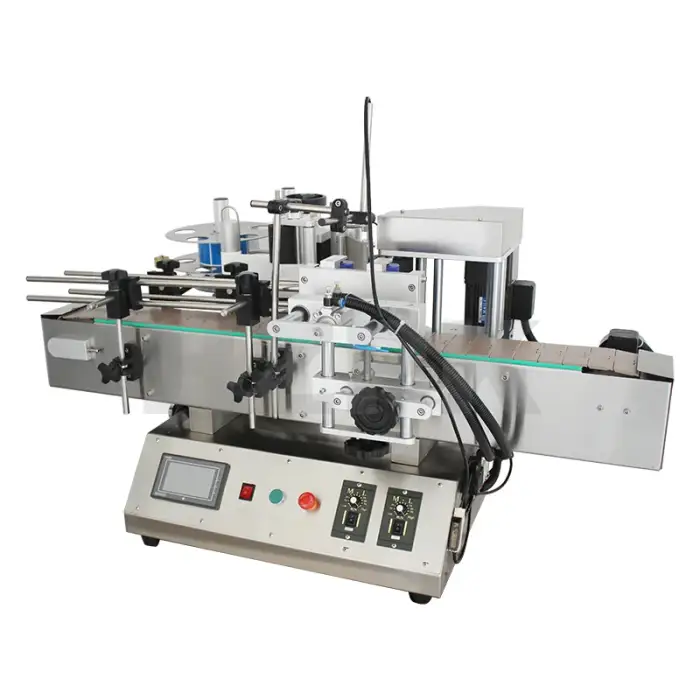
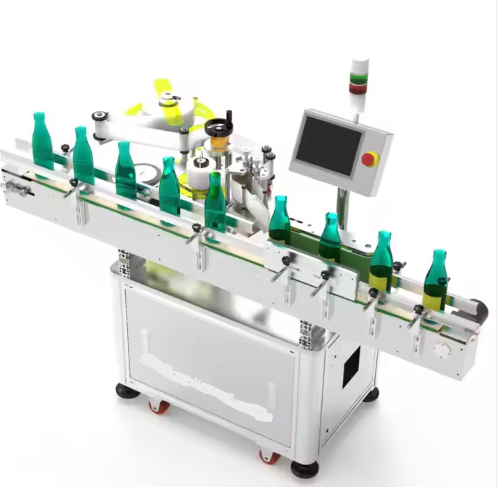
Automatic Box Strapping and Binding Packaging Machine
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Boxing Machines
- SKU : 1600861637270

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 11 May, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is an Automatic Box Strapping and Binding Packaging Machine?
A machine that automatically applies and secures straps around cartons, boxes or bundles to stabilize, close and prepare them for transport — combining strapping (looping a strap) and binding (tightening/secure finishing) functions in a single unit.
2. Which strap types and sizes does the machine support?
Most models support polypropylene (PP) and polyester (PET) straps; some can be configured for steel straps. Common strap widths are 9–19 mm (3/8"–3/4"), but widths and thicknesses are selectable or customizable depending on the model.
3. What industries and applications is it suitable for?
Suitable for e‑commerce packaging, logistics and distribution centers, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, electronics, manufacturing and any operation that needs consistent, fast carton sealing, pallet bundling or bundle binding.
4. How fast is the machine (throughput)?
Throughput depends on model, strap cycle, box size and line configuration; typical automatic machines process from several to several dozen packages per minute. Inline installations and optimized settings increase effective throughput.
5. What carton sizes and weights can it handle?
Many machines handle a wide range of carton dimensions via adjustable guides and straps. Standard models fit small to large boxes; heavy‑duty models are available for heavier packages. Exact limits depend on the chosen model and can be specified for your application.
6. What are the power and utility requirements?
Requirements vary by model. Single‑phase (220–240 V) or three‑phase (380–480 V) power options are common. Some machines also require compressed air (for pneumatic tensioning) — typical air pressure is 5–7 bar. Exact specs are provided on the machine data sheet.
7. Is the machine fully automatic or does it require operator intervention?
There are fully automatic versions that integrate with conveyors and trigger by sensors, and semi‑automatic versions that require operator feeding. Features like automatic strap feed, cutting, tensioning and ejection minimize operator involvement on fully automatic units.
8. Can it be integrated into an existing production line?
Yes. These machines are designed for inline integration and typically offer conveyor interfaces, PLC control, electrical and signaling options (e.g., 24 V I/O, Ethernet/IP, Profinet) to communicate with upstream and downstream equipment.
9. What safety features are included?
Common safety features include emergency stop buttons, safety guards and covers, interlocks, light curtains or area scanners (optional), and compliant electrical safety to CE/UL standards depending on region and configuration.
10. What maintenance is required and how often?
Routine maintenance includes cleaning strap paths, lubricating moving parts as specified, checking and replacing wear parts (tensioner, blades, rollers), and inspecting electrical connections. A basic maintenance schedule is monthly with more frequent checks in high‑use environments.
11. Are spare parts and after‑sales support available?
Yes. Manufacturers typically supply spare parts (strapping heads, sensors, motors, cutters), technical documentation, remote support, on‑site service and operator training plans. Availability and response times depend on supplier and service contract.
12. Can the machine be customized with additional features?
Yes. Common options include different strap heads, higher‑capacity strap dispensers, automatic strap coil changers, turntables, reject/pushers, carton flippers, label printers, product sensors, and customized tensioning profiles to match your product and packaging needs.
13. What certifications and quality standards do these machines meet?
Many machines are designed to meet CE, UL, and other regional safety and electrical standards. Quality and manufacturing certifications (e.g., ISO) depend on the supplier — check the machine datasheet or ask the vendor for certification documents.
14. How do I get a quote and what is the typical lead time?
Contact the supplier with your application details (box sizes, throughput, strap type, line integration needs). Lead times vary by model, customization and order size but typically range from a few weeks to a couple of months; shorter lead times may be possible for standard models in stock.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading