B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
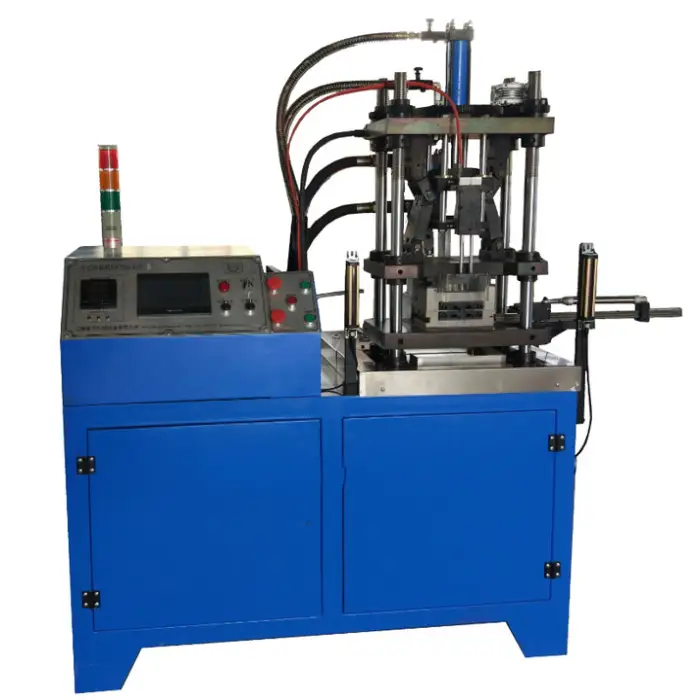
Automatic 20 Ton Chamber Zinc Die Casting Machine
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- SKU : 1600457677337

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 02 Apr, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What materials can I cast with the Automatic 20 Ton Chamber Zinc Die Casting Machine?
This is a hot-chamber die casting machine primarily designed for zinc and other low‑melting‑point alloys (e.g., some zinc‑based alloys, tin, lead). It is not recommended for high‑melting‑point alloys such as aluminum — check with the supplier for alloy compatibility and process settings.
2. What does the '20 Ton' rating refer to?
The '20 Ton' designation refers to the machine’s clamping/locking capacity (approx. 20 tons), suitable for producing small to medium zinc parts where this locking force is sufficient to keep the die closed during injection.
3. What are the main technical specifications I should know?
Key specs supplied: hot chamber type; die block thickness 55 mm (min and max listed as 55 mm — please confirm); ejection force 30 kN; ejection stroke 30 mm; motor power 5.5 kW; machine weight 1000 kg; wire diameter range 1.0–3.5 mm; production rate listed as "1.2–1.6 w pcs/day" (please confirm meaning).
4. The spec shows Max and Min Die Block Thickness both as 55 mm — what does that mean?
The listing shows a die block thickness of 55 mm. Because max and min are identical in the spec, confirm with the supplier whether the die block thickness is fixed at 55 mm or if a range is available or configurable.
5. What is the machine’s production capacity and cycle time?
The datasheet lists a production rate of "1.2–1.6 w pcs/day," which is unclear. Actual capacity depends on part geometry, shot weight, cycle time and process optimization. Ask the supplier for sample trials or cycle‑time estimates based on your part drawings to get an accurate output figure.
6. What are the electrical and foundation requirements?
Rated motor power is 5.5 kW. Voltage, phase and frequency requirements and recommended foundation specifications are not listed — request detailed electrical schematics and foundation drawings from the supplier prior to installation.
7. What are the machine dimensions, packaging size and shipping weight?
The spec provides a single package size of 1450 x 1000 x 1720 (units as listed) and a single gross weight of 1000 kg. Because package units may be misstated, confirm whether those dimensions are in mm or another unit before arranging transport.
8. How many machines can you supply and what is the lead time?
The supply ability is listed as 3 sets per month. Lead time for a single unit will depend on order queue, customization and shipping — confirm with the supplier when placing an order.
9. What safety and quality assurances are included?
The machine is described as having user‑friendly controls and durable construction. The seller provides a machinery test report and video outgoing inspection. For safety specifics (guards, interlocks, emergency stop, CE/ISO compliance), request the machine’s safety documentation and certificates from the supplier.
10. What tooling and mold requirements are needed?
Tooling must be designed for hot‑chamber zinc die casting and match the machine’s die block thickness and clamping force. Provide your toolmaker with the machine’s confirmed die dimensions, ejection stroke (30 mm) and ejection force (30 kN). Coordinate with the supplier to verify mold compatibility.
11. What maintenance is required and are spare parts available?
Regular maintenance typically includes lubrication of moving parts, inspection/replacement of seals and nozzles, routine cleaning of injection areas and checks on hydraulic/electrical systems. Confirm recommended maintenance intervals and spare‑parts availability (critical wear parts such as tips, needles, o‑rings and heaters) with the manufacturer or distributor.
12. Is operator training provided?
The machine is described as easy to operate with user‑friendly controls. Many suppliers offer operator and maintenance training (onsite or remote) — ask the seller whether training is included or available as an option.
13. Can this machine be integrated with automation (robotic part removal, conveyors)?
Integration is often possible but depends on control interfaces and available automation options. Discuss your automation requirements (robot pick‑and‑place, conveyors, part washing) with the supplier so they can specify compatible interfaces or add‑on packages.
14. What types of parts and industries is this machine best suited for?
Typical applications listed include automotive parts, household items, electronic components, industrial machinery parts and decorative fixtures — generally small to medium zinc castings requiring high productivity and repeatability.
15. How do I request a quote, sample trial or more technical information?
When requesting a quote or sample trial, provide part drawings (CAD), desired alloy, expected annual volume, target cycle time, and any quality standards. Ask the supplier for detailed specs, electrical/foundation drawings, warranty terms, test reports and options for acceptance trials or sample parts.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading