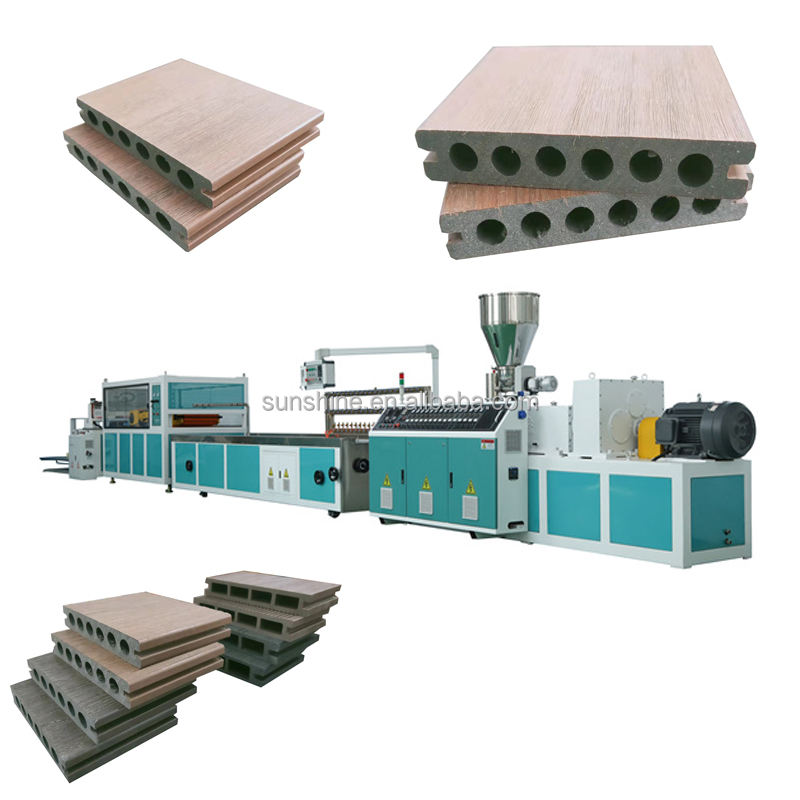
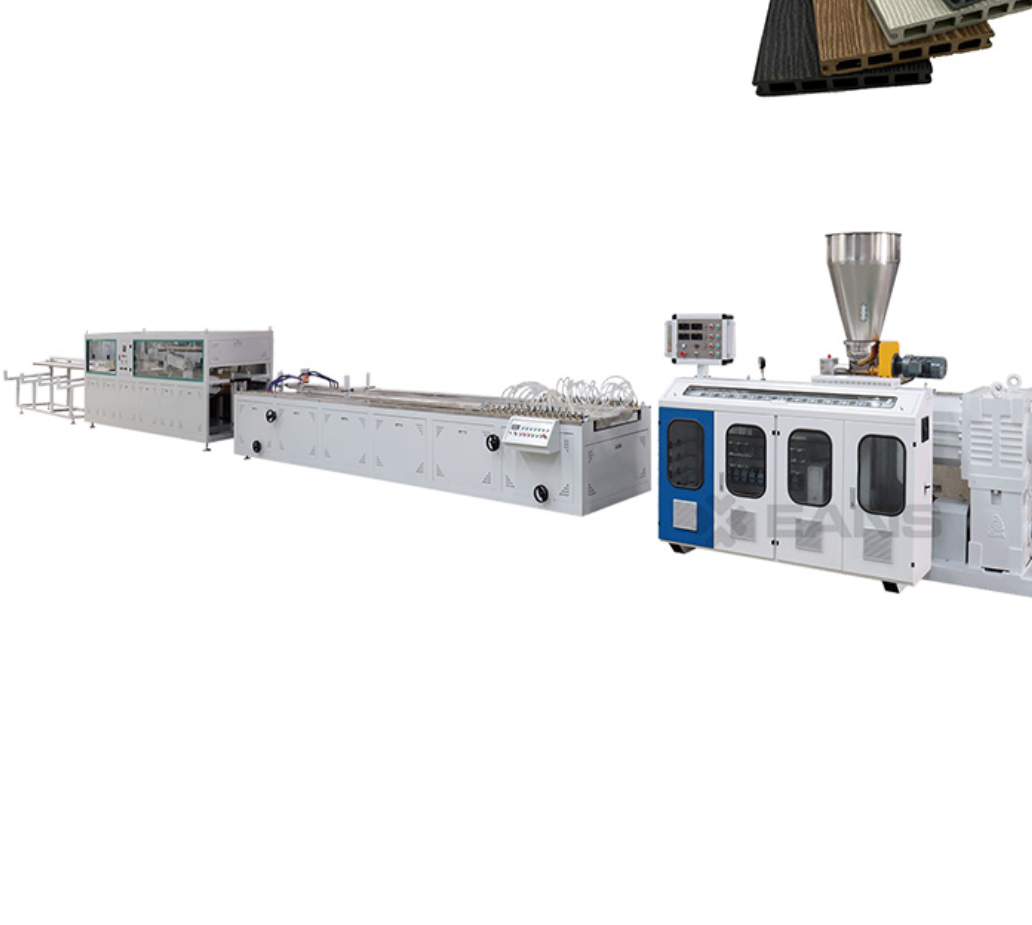
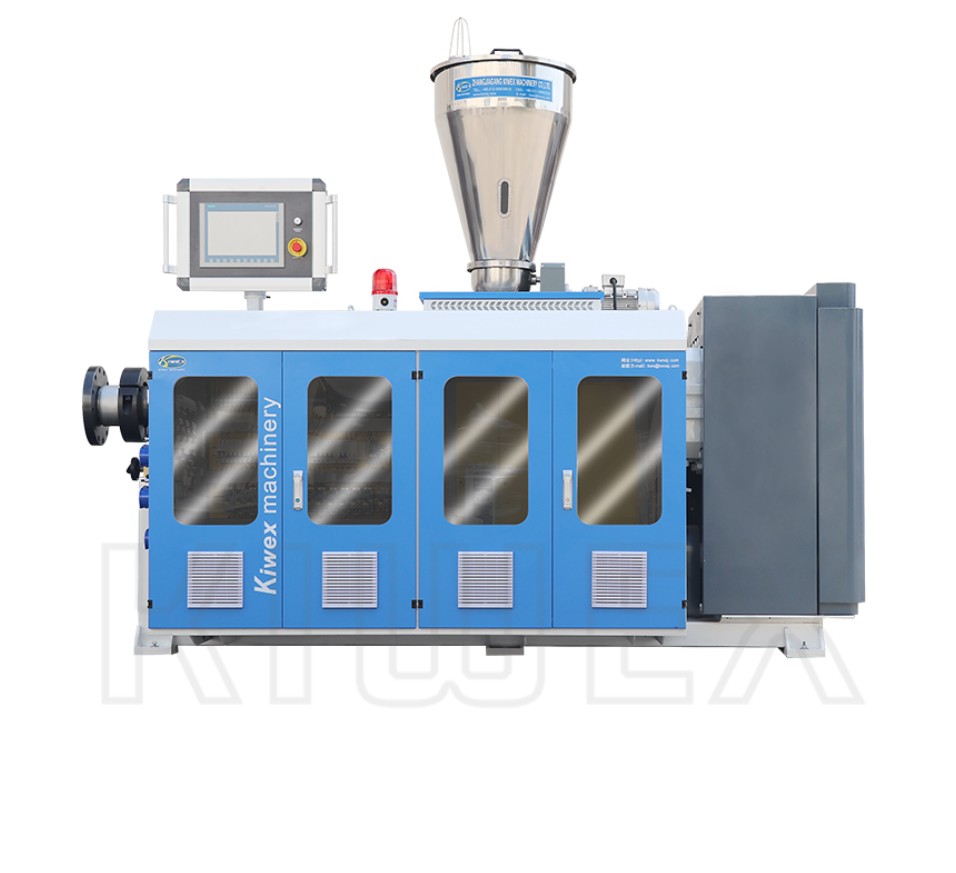
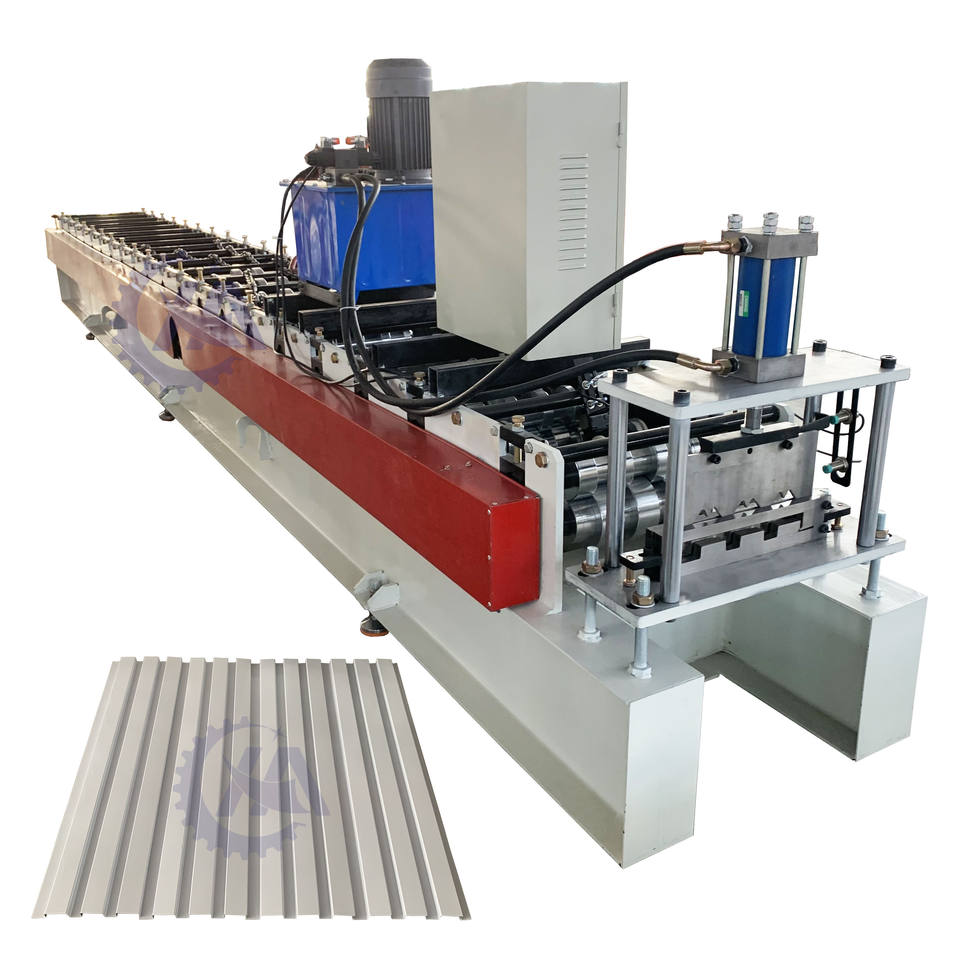
B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 11 May, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What types of fabrics can an industrial sewing machine handle?
Industrial sewing machines are designed for a wide range of materials, from lightweight fabrics (silk, polyester) to heavy-duty materials (denim, canvas, upholstery fabric, leather). Choose the machine model and needle type rated for the specific fabric thickness and hardness.
2. What stitch types do industrial sewing machines support?
Common industrial machines support lockstitch and chainstitch. Specialized models may offer overlock, coverstitch, blindstitch, and multi-needle configurations. Check the model specifications to confirm supported stitch types.
3. What is the typical sewing speed of an industrial sewing machine?
Sewing speeds vary by model and application, but many industrial machines run between 2,000 and 6,000 stitches per minute. Heavy-duty or specialized processes may operate at lower speeds to maintain stitch quality.
4. Does the machine include a motor, and what motor types are available?
Most industrial sewing machines are sold with either a clutch motor (traditional) or a servo motor (energy-efficient, quieter, and offers better speed control). Some suppliers offer the option to upgrade or change motor types.
5. What power/voltage requirements should I expect?
Industrial machines typically require 110–120V or 220–240V, single-phase or three-phase depending on the motor and region. Verify the machine's electrical specifications and power supply compatibility before installation.
6. What maintenance is required to keep the machine running well?
Regular maintenance includes daily cleaning of lint and debris, periodic oiling/lubrication per the manufacturer's schedule, replacing needles and bobbins as needed, and routine inspection and adjustment of tension and timing. Professional servicing is recommended for more complex repairs.
7. How do I choose the correct needle and thread?
Select needle size and type based on fabric weight and material (e.g., universal, leather, ballpoint). Use thread strength and thickness appropriate for material and stitch type—polyester threads are common for general use; bonded nylon or heavy-duty polyester for thick materials.
8. Are spare parts and accessories available?
Yes, most industrial sewing machines have readily available spare parts (needles, bobbins, presser feet, belts, motors) and accessories (rollers, walking feet, extensible tables). Availability depends on brand and model—check with the supplier for specific part numbers.
9. What safety features should I expect?
Safety features may include finger guards, belt covers, emergency stop switches, auto shutoff for overheating, and CE/UL safety compliance. Proper training and personal protective equipment (PPE) are also important for safe operation.
10. Do industrial sewing machines come with a warranty?
Warranties vary by manufacturer and seller. Typical warranties cover manufacturing defects for 1–2 years on the machine head and a shorter period for electrical components. Confirm warranty terms, what is covered, and any required registration.
11. Can the machine be configured for automated or multi-needle production?
Yes. Many industrial machines can be configured with multi-needle heads, automatic thread trimmers, programmable stitch patterns, and robotic feeders for high-volume or automated production. Check model options for automation capabilities.
12. How much workspace and what accessories are needed for installation?
Installation typically requires a sturdy table or stand, adequate floor space for operator movement, and clearance for attached accessories (knees, feeders). Ensure access to the proper power outlet and consider lighting and ventilation. Exact dimensions depend on the model and attachments.
13. What training is required to operate and maintain the machine?
Operators should be trained on threading, tension adjustment, needle replacement, basic troubleshooting, and safety procedures. Many suppliers offer on-site or online training, manuals, and video tutorials. For complex repairs, factory-trained technicians are recommended.
14. What is the lead time and shipping process for industrial sewing machines?
Lead times vary by stock availability, customization, and shipping destination—ranging from a few days for stock models to several weeks for custom or backordered units. Machines are typically crated and shipped by freight; confirm freight terms, insurance, and installation options with the seller.
15. What should I do if the machine is skipping stitches or breaking threads?
Common causes include a bent or dull needle, incorrect needle size/type, poor-quality thread, incorrect tension settings, or timing issues. Start by replacing the needle, rethreading the machine, and checking tension. If the problem persists, consult the manual or contact a qualified technician.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading
















