B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
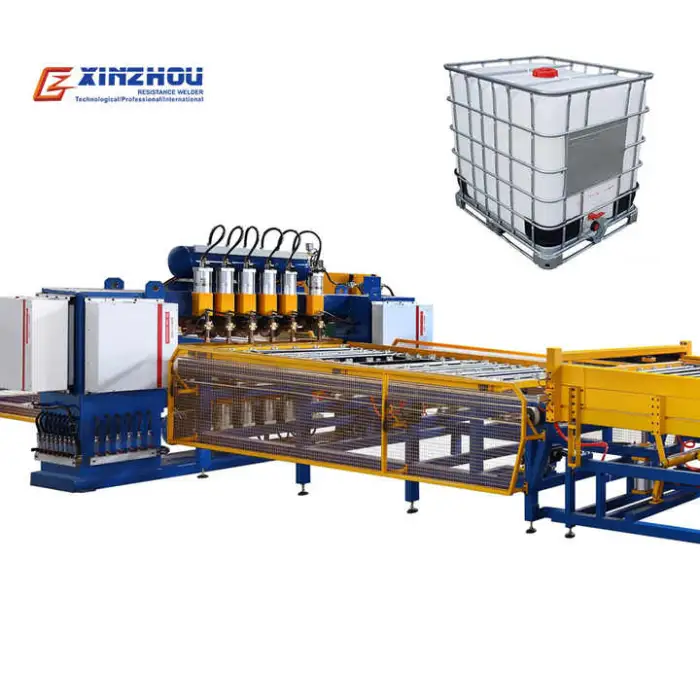
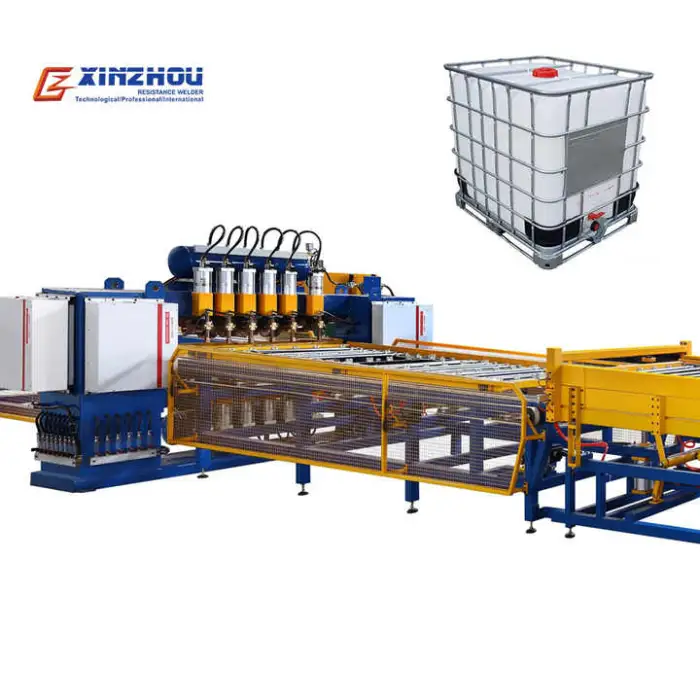
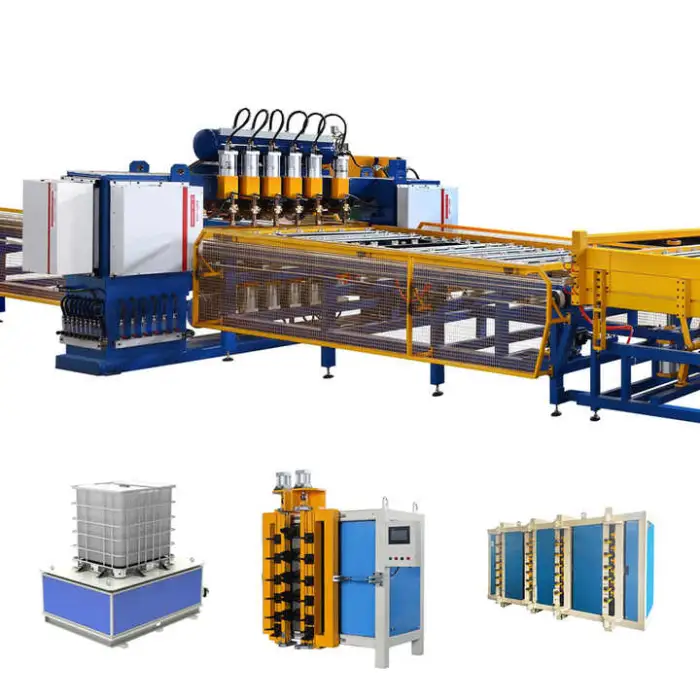
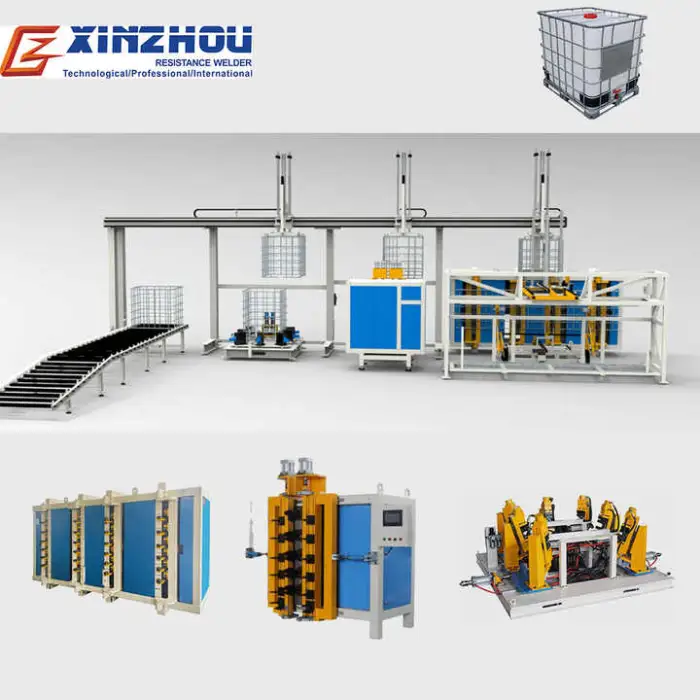
IBC Cage Tank Frame Welding Machine Production Line for Efficient Metal Processing
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- SKU : 1600950422109

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 01 Apr, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is the IBC Cage Tank Frame Welding Machine Production Line designed for?
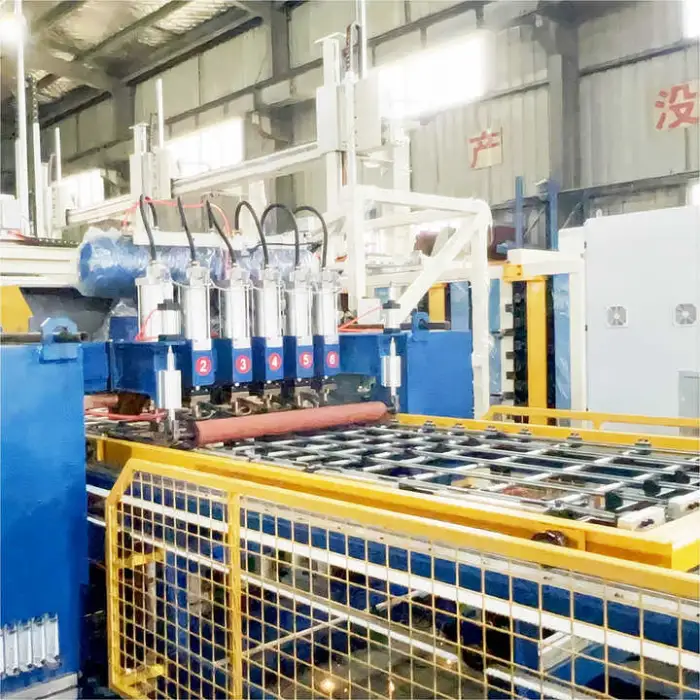
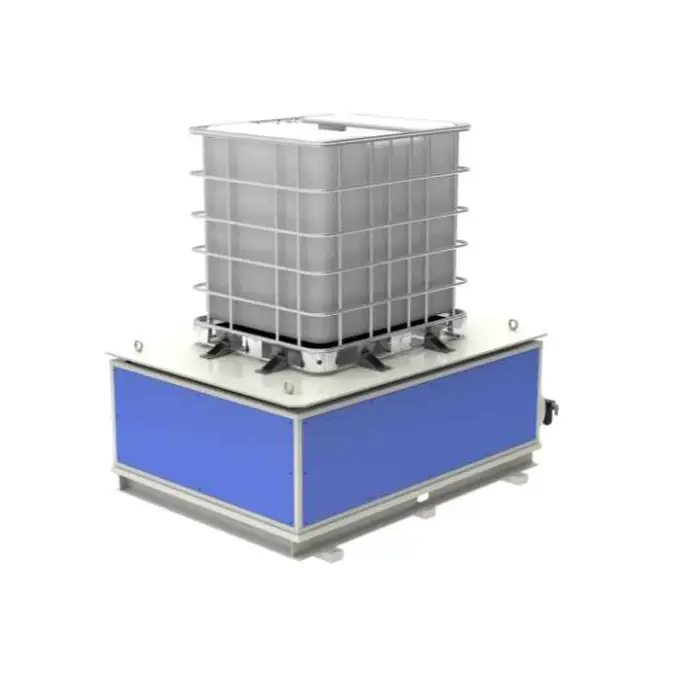
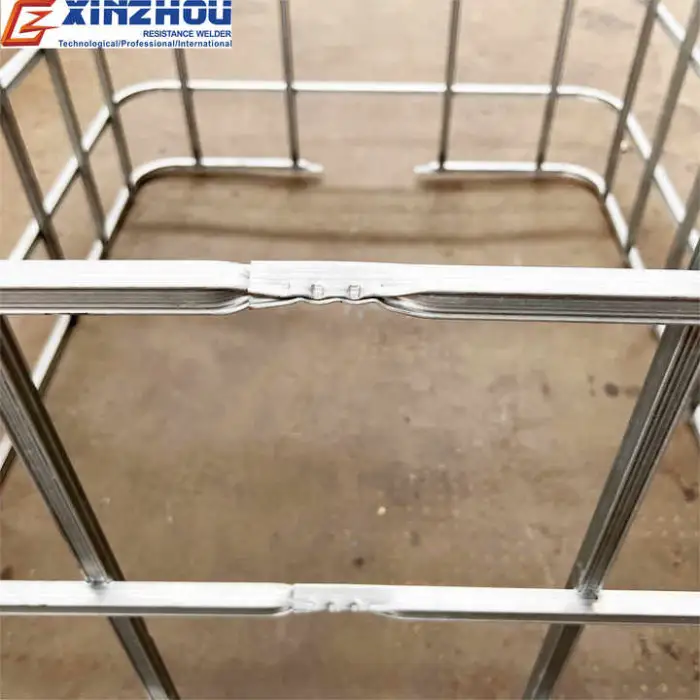
This production line automates welding, bending and grinding to manufacture IBC (intermediate bulk container) cage frames used for chemical storage and transport, improving throughput, consistency and product quality compared with manual methods.
2. What are the main specifications of the production line?
Key specs include: product name IBC Cage Frame Production Line; automatic welding function; stainless steel construction; automatic grade: Auto; voltage: 380V; power: 1600W; capacity: 80 (manufacturer-specified); dimensions: 16m x 3.5m x 2m; supply ability: 20 sets per month.
3. What does the listed 'Capacity: 80' mean?
'Capacity: 80' is the manufacturer's nominal capacity figure. It may refer to units per shift/day or a batch figure depending on configuration. Confirm with the supplier for the exact unit of measure and expected throughput under your production parameters.
4. What are the electrical requirements?
The line requires a 380V power supply (typically three-phase). The listed power is 1600W. Have your electrical contractor verify site supply, wiring, protective devices and grounding to meet local electrical codes and the machine's startup/load requirements.
5. What is the floor space and site preparation required?
Overall dimensions are approximately 16m (L) × 3.5m (W) × 2m (H). You should allow additional clearance for material handling, operator access, maintenance and ventilation. A level concrete floor with appropriate load-bearing capacity and access for forklifts/cranes is recommended.
6. Which materials and product types can this line process?
It is optimized for steel IBC cage frames (stainless steel construction for the line itself). It supports common mild and stainless steels used for cages; for other alloys or thicknesses, consult the supplier to confirm compatibility and adjust welding parameters.
7. What machines and features are included in the line?
The production line includes automatic welding equipment plus integrated bending and grinding machines, PLC control for coordinated operation, and a compact, durable stainless steel structure to support continuous production.
8. Can the system be customized or integrated into an existing production line?
Yes — most suppliers offer customization for cage dimensions, welding programs, material handling interfaces and PLC I/O for integration. Discuss your product specs and existing line control protocols with the vendor to define required modifications.
9. What is the typical production throughput and quality consistency?
Throughput depends on product design, cycle settings and material handling. The automated welding and integrated prep (bending/grinding) provide much more consistent weld quality and higher repeatable output versus manual methods. Ask the supplier for sample cycle times and case studies for comparable products.
10. What is involved in installation and commissioning?
Installation typically includes site positioning, electrical connection, grounding, air/ventilation setup (if required), mechanical leveling and alignment, PLC parameterization and commissioning trials. Most manufacturers provide on-site commissioning or remote support.
11. Is operator training provided?
Suppliers commonly provide operator and maintenance training covering machine operation, PLC HMI use, routine maintenance, basic troubleshooting and safety procedures. Confirm training scope, language and whether it is on-site or remote when placing an order.
12. What routine maintenance and consumables are required?
Routine tasks include cleaning, lubrication of moving parts, inspection and replacement of welding consumables (electrodes, nozzles), checking grinding/bending tooling, and verifying PLC/servo parameters. Establish a spare-parts list for fast-moving items and follow the manufacturer's maintenance schedule.
13. What safety measures and certifications should I expect?
Expect standard machine guarding, emergency stops, interlocks, proper ventilation for welding fumes and PPE requirements for operators. Certification availability (CE, ISO, etc.) varies by supplier and market — request up-to-date certificates and safety documentation prior to purchase.
14. How are spare parts, technical support and warranty handled?
Most manufacturers supply spare parts, remote technical support and after-sales service contracts. Warranty terms vary — commonly 12 months but confirm exact coverage, response times and availability of local service engineers. Given the monthly supply ability (20 sets), ask about lead times for replacement parts.
15. What are lead times and how many units can you supply?
The quoted supply ability is 20 sets per month. Actual lead time depends on order size, customization and logistics. Contact the supplier with your order details to get an accurate delivery schedule and shipping options.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading



















