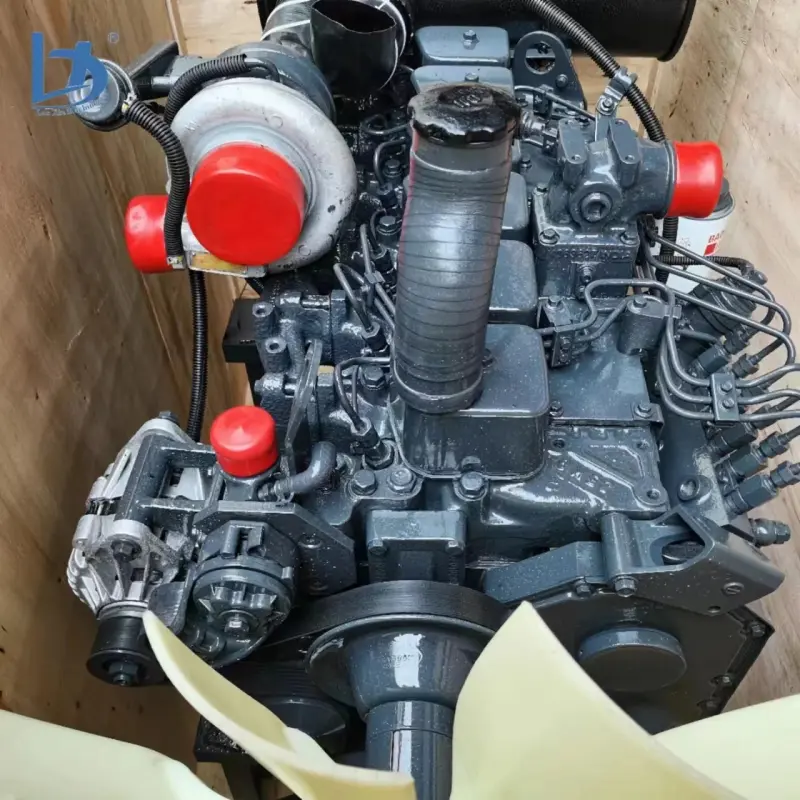
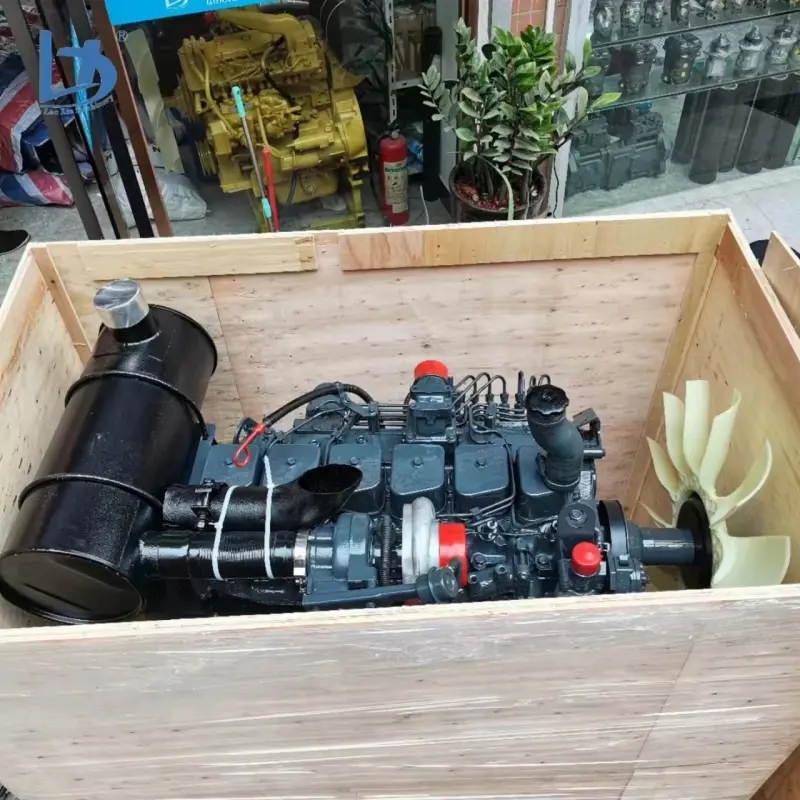
B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 18 Apr, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
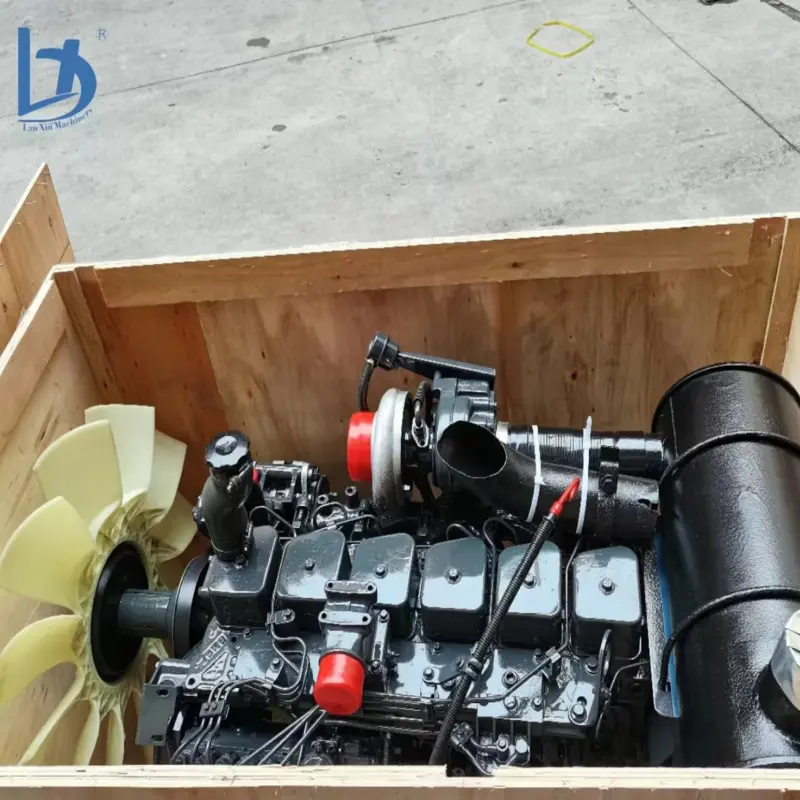
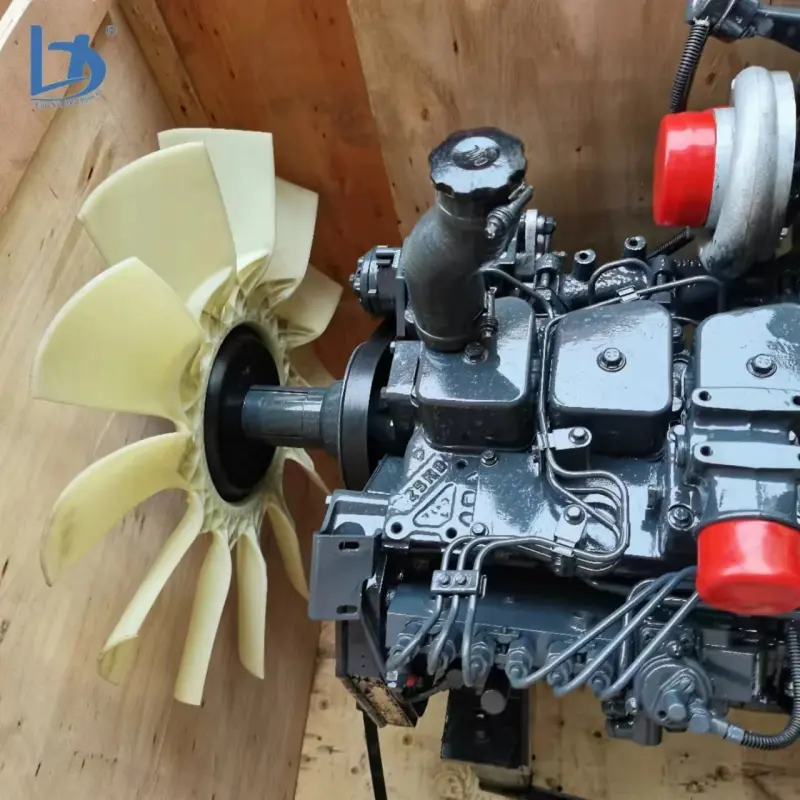
1. What is a Cummins Diesel Engine?
A Cummins diesel engine is a diesel-fueled internal combustion engine built by Cummins Inc. for use in applications such as trucks, buses, RVs, industrial equipment, marine vessels, and standby or prime power generators.
2. Which fuels can I use in a Cummins diesel engine?
Use diesel fuel that meets local specifications (e.g., ULSD in the United States). Avoid gasoline and fuels containing excessive water or contaminants. For biodiesel blends, follow Cummins' published fuel compatibility guidelines.
3. How do I identify my Cummins engine model and serial number?
The engine data plate (or tag) attached to the engine housing contains the model number, serial number (ESN), and other identifying data. You can also find the ESN in the engine documentation or by contacting your dealer with vehicle/vessel information.
4. What routine maintenance does a Cummins diesel engine require?
Regular maintenance typically includes oil and filter changes, fuel filter replacement, air filter inspection/replacement, coolant checks, and inspection of belts, hoses and electrical connections. Follow the specific maintenance schedule in the engine's service manual for interval recommendations.
5. How often should I change the engine oil?
Oil-change intervals depend on the engine model, duty cycle and operating conditions. Refer to the engine service manual for recommended hours or mileage intervals. Severe or dusty conditions may require more frequent changes.
6. Are Cummins engines compatible with my vehicle or application?
Compatibility depends on the specific engine model, mounting, transmission interface, controls/ECM, cooling system and emissions equipment. Consult Cummins technical documentation or an authorized Cummins dealer/installer to confirm fitment and necessary modifications.
7. What kind of warranty comes with a Cummins diesel engine?
Warranty coverage varies by engine model, market and whether the engine is new, remanufactured or used. Typical warranties cover defects in materials and workmanship for a specified time or hours. Check the warranty statement provided at purchase or contact your Cummins dealer for details.
8. How can I obtain genuine Cummins parts and filters?
Purchase genuine parts, filters and consumables from an authorized Cummins dealer or distributor. Using genuine parts helps ensure performance, emissions compliance and maintains warranty coverage.
9. What should I do if my Cummins engine won't start?
Check battery charge and connections, fuel supply and filter condition, fuel shutoff valves and fuses. For electronically controlled engines, an ECM fault code can guide diagnosis. If basic checks don't resolve the issue, contact an authorized Cummins service center for diagnostics.
10. Why is my Cummins engine producing excessive smoke?
Excessive smoke can indicate issues such as incorrect fuel, clogged air filter, injector problems, turbocharger faults, or EGR/DOC/DPF system malfunctions. Collect fault codes and consult a qualified technician for a proper diagnosis.
11. How long can I expect a Cummins diesel engine to last?
With proper maintenance and operation, Cummins diesel engines can provide tens of thousands of operating hours. Actual life varies by model, application, duty cycle and how well the engine is maintained.
12. Do Cummins engines meet emissions regulations?
Many Cummins engines are certified to meet regional emissions standards (EPA, CARB, EU Stage, etc.). Emissions compliance depends on the specific engine configuration and any aftertreatment systems installed. Verify the engine's emissions label and certification documentation for your region.
13. Can I get software updates or reprogram the engine control module (ECM)?
Authorized Cummins dealers use Cummins INSITE and other tools to update ECM software, calibrations and to read/clear diagnostic trouble codes. ECM reprogramming should be performed by qualified personnel to maintain performance and emissions compliance.
14. Where can I get service or technical support for my Cummins engine?
Contact your local authorized Cummins dealer or service center for maintenance, repairs and technical support. Cummins also provides technical documentation, manuals and support through its dealer network.
15. What safety precautions should I follow when working on a Cummins diesel engine?
Follow the safety procedures in the service manual: work on a cool, well-ventilated engine; isolate the battery and fuel supply; relieve pressure from fuel and cooling systems before opening; use appropriate PPE; and have qualified personnel perform electrical, fuel system or emissions-system work.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories
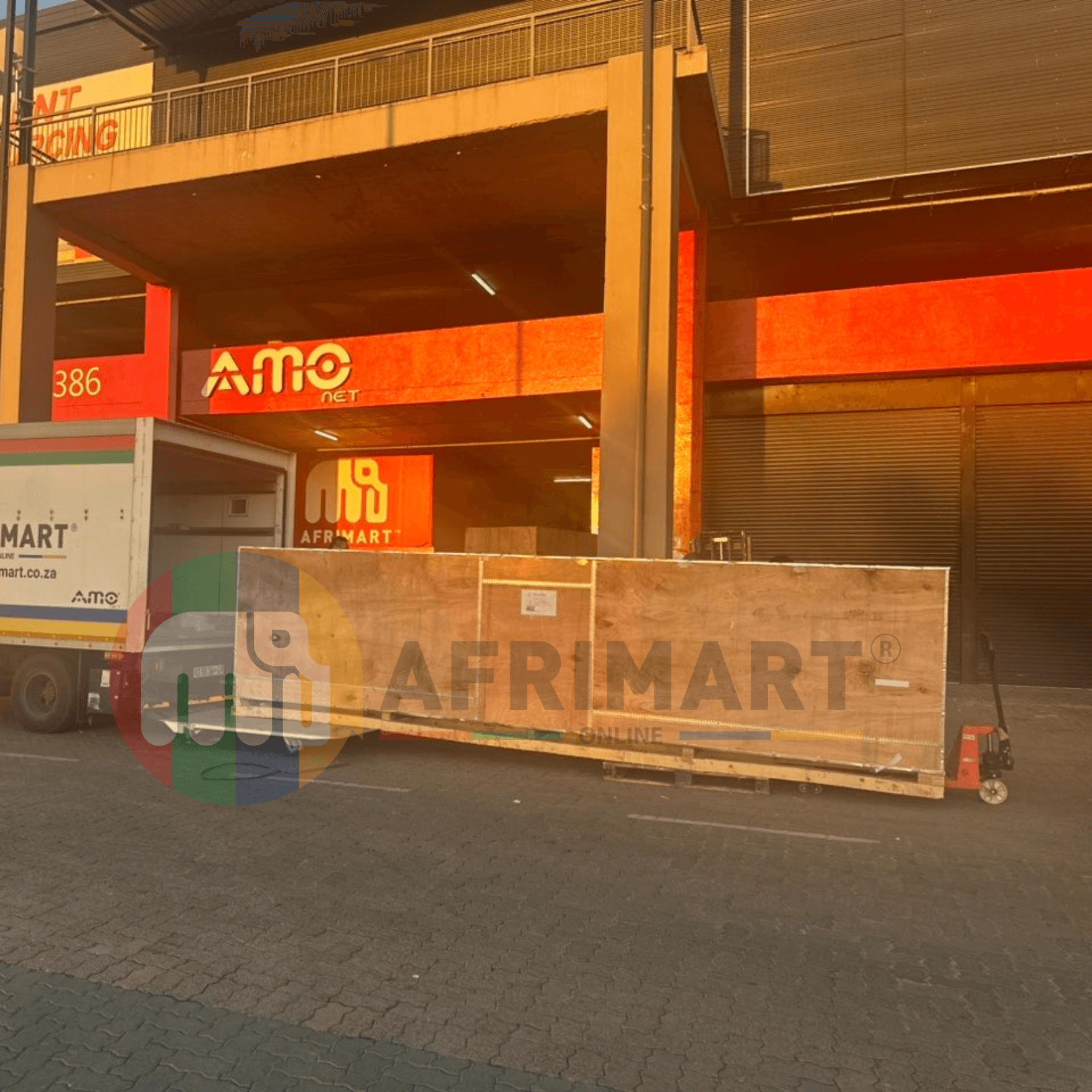

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment
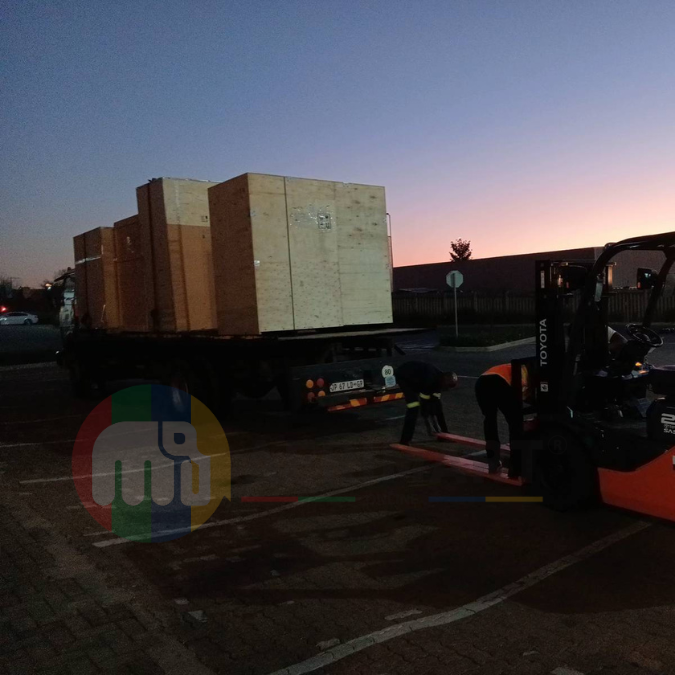

Mining Equipments
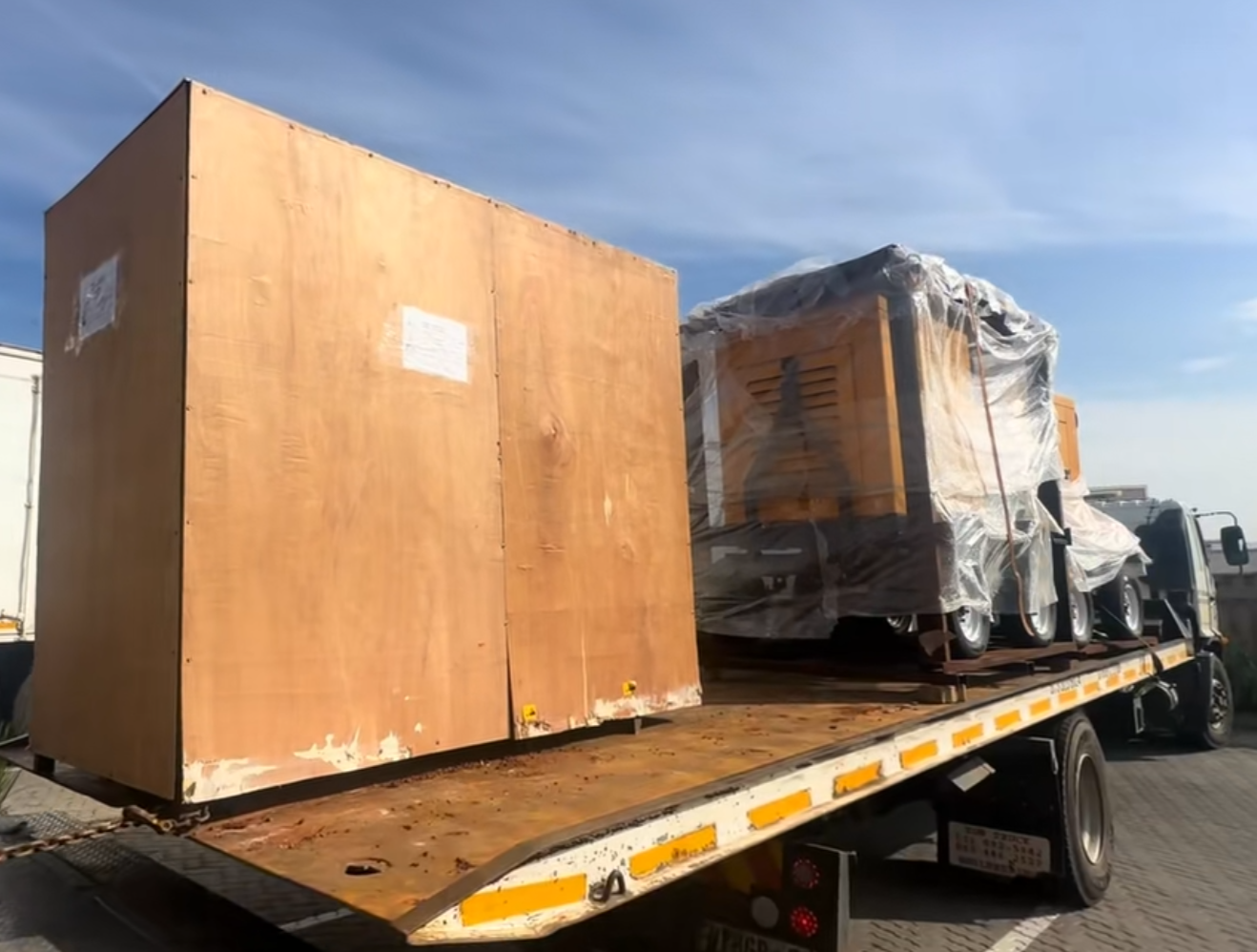

Food Processing Machine
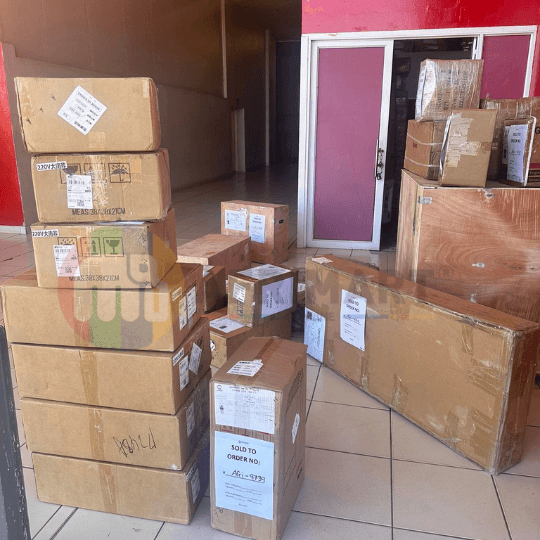

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders
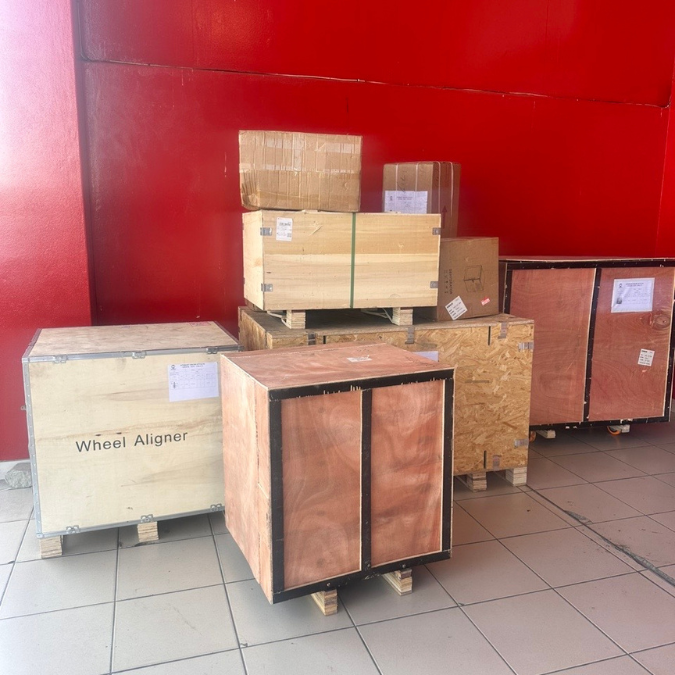

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading