B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
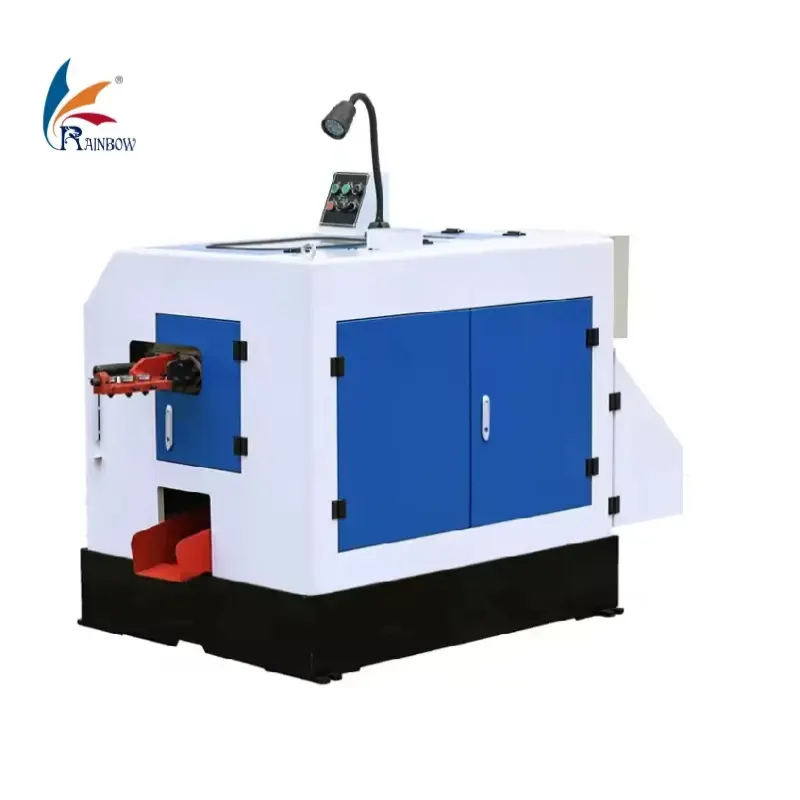
Automatic Cold Forging Bolt Making Machine
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- SKU : 1601094816194

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 22 Apr, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is an Automatic Cold Forging Bolt Making Machine (cold heading machine)?
A cold heading machine (automatic cold forging bolt making machine) shapes metal wire (carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper) into fastener components by feeding, shearing and pressing the blank into dies using a crankshaft/slider mechanism. It automates production of heads, stems and related parts without melting the metal.
2. What types of fasteners and parts can this machine produce?
It can produce a wide variety of fasteners and related parts including truss, countersunk, pan, flat, hexagon, socket, button and cap heads; set screws, wood/chipboard/self-tapping screws, bolts, nuts (square, weld, cap, blind, hex socket lockup), washers, expansion anchors, motorcycle/bicycle pins and rollers, oil plug screws and many custom shapes with proper tooling.
3. Which raw materials are suitable for use in this machine?
Typical materials are carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum and copper wire. Material grade, wire hardness and lubrication affect formability — consult the manufacturer for recommended alloys and pre-treatment for specific parts.
4. What is the production speed (output) range I can expect?
Output depends on model, blank size and part complexity. Typical rates range from about 25–200 pieces per minute across the model range (small-diameter models reach up to 150–200 pcs/min; large models run slower, e.g., 25–80 pcs/min).
5. How do I choose the right model for my part dimensions?
Select a model based on maximum blank diameter, maximum blank length, cutoff length and required stroke. The product data lists many models (RSH3–RSH16) with max blank diameters from 3 mm up to 16 mm and corresponding blank/cutoff lengths and strokes. Provide your target blank diameter, length and part drawing to the supplier for exact model recommendation.
6. What are the machine power, footprint and weight requirements?
Main motor power ranges approximately from 1.1 kW (1.5 HP) up to ~22 kW (25 HP) depending on model. Footprint and height vary by model (typical machine sizes are roughly 1.4–6.5 m long, 0.75–2.25 m wide, 0.9–2.1 m high). Weights range from ~650 kg up to ~21,000 kg for the largest models. Confirm site power and floor load capacity before installation.
7. What safety features and operator protections are provided?
Cold heading machines include guarding around moving parts, emergency stop controls, interlocks on access panels and safe feed mechanisms. Operators should follow lockout/tagout procedures, wear PPE and receive training. Specific safety options and guarding levels can be specified with the supplier.
8. How long does tooling (dies/cutters) last and can I get replacements?
Tooling life depends on material, production volume and maintenance. With proper die material, heat treatment and lubrication, dies can last many thousands to millions of cycles. The manufacturer supplies replacement die sets, cutters and refurbishment services; provide part drawings and production parameters to size tooling correctly.
9. What maintenance is required and how often?
Regular maintenance includes daily cleaning, lubrication of bearings and guideways, periodic checking of crankcase oil, inspection of dies and cutters, and tightening of fasteners. A preventive maintenance schedule (daily/weekly/monthly) and spare-parts list will be supplied by the manufacturer. Planned downtime for die inspection and replacement is recommended.
10. Can the machine be integrated with automatic wire rolling and feed systems?
Yes. These cold heading machines are designed to work in tandem with automatic wire rolling/feeding machines. Integration options include in-line wire feeders, straighteners and automatic part conveyors. The supplier can provide or adapt interfaces for your existing line.
11. How long is lead time and what are shipping/installation options?
Lead time varies by model, tooling complexity and customization — typically a few weeks to several months. The manufacturer usually offers packing for export, sea/air freight assistance, on-site installation, commissioning and operator training (terms depend on the order). Confirm lead time and service scope when requesting a quote.
12. What tolerances and part quality can I expect?
Dimensional tolerances depend on part geometry, tooling accuracy, material and process control. Cold heading typically achieves tight dimensional control suitable for most fastener standards. For critical tolerances or surface finish/hardness requirements, supply detailed drawings and functional requirements so tooling and process can be engineered accordingly.
13. Is customization available (special dies, nonstandard parts, automation add-ons)?
Yes. The manufacturer provides customization of die sets, head forms, feeders and automation (e.g., part transfer, inspection, packaging). Discuss required part profiles, volumes and any downstream automation needs to get a tailored solution and quote.
14. What after-sales support, training and warranty are offered?
The manufacturer provides technical support, installation and operator/maintenance training as part of the purchase agreement. Warranty terms, spare-parts availability and service contracts vary — ask the supplier for specific warranty duration, coverage and service-level options.
15. How do I get a quote — what information is needed?
Provide part drawings (2D/3D), target material and hardness, required production rate (pcs/min), expected annual volume, preferred model size constraints and any automation needs. With these details the supplier can recommend a model, tooling solution and provide pricing, lead time and service options.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading















