B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
Tire Recycling Machine: Efficient Solution for Rubber Powder Production from Waste Tires
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Industrial Machinery
- SKU : 1601015686464

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 30 Apr, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What does the Tire Recycling Machine do?
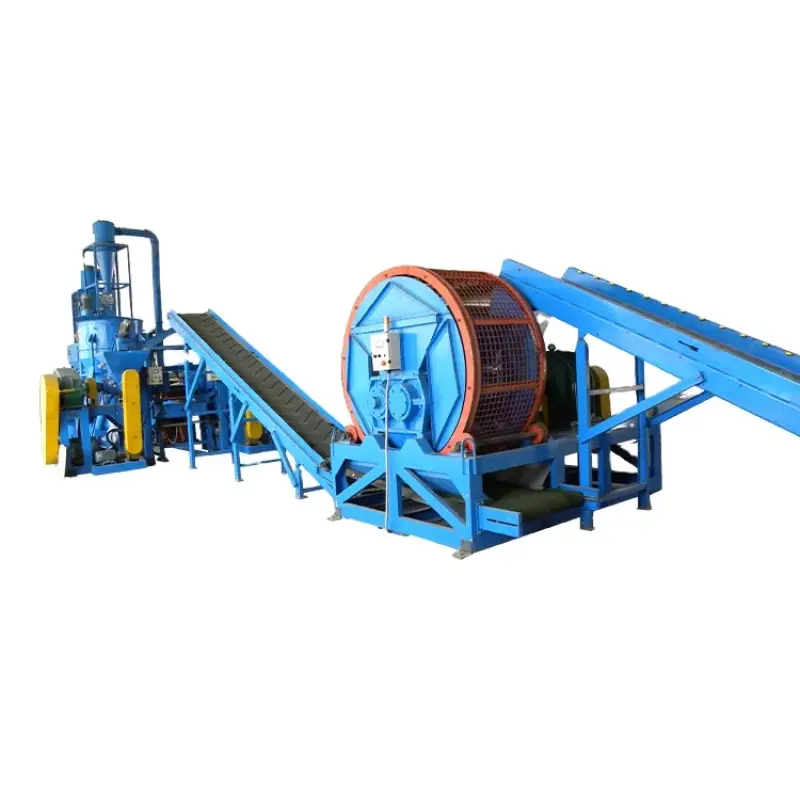
It recycles waste tires into rubber powder (20–100 mesh) by debeading (removing steel), shredding, crushing and fine grinding. The staged process produces rubber granules and then superfine powder for reuse.
2. What is the typical process flow of the plant?
Typical flow: SL-1200 Double Hook Tire Debeader (remove steel bead) → ZPS-1200 Tire Shredder (50×50 mm shreds) → PSJ-900 Rotating Crusher (8–12 mm granules) → CSJ-600/800 Crusher (1–4 mm granules) → CXFJ-28 Powder Mill (30–100 mesh final powder).
3. What are the main models and their roles in the line?
Key machines: SL-1200 (debeader), ZPS-1200 (primary shredder), PSJ-900 (rotating crusher to 8–12 mm), CSJ-600/800 (grind to 1–4 mm), CXFJ-28 (rubber powder mill to 30–100 mesh).
4. What capacities can I expect from each machine?
SL-1200: 60–100 pcs/h (≤1200 mm tires). ZPS-1200: 2000–4000 kg/h (50×50 mm output). PSJ-900: 1000–1500 kg/h (8–12 mm output). CSJ-600/800: 300–400 / 500–800 kg/h (1–4 mm output). CXFJ-28: 40–150 kg/h (30–100 mesh powder).
5. What final powder sizes are available and their common applications?
20–100 mesh (product examples): 5–10 mesh (2–4 mm) for playgrounds/tiles; 10–20 mesh for floor tiles and sports courts; 30–40 mesh for reclaimed rubber, asphalt additives, gloves; 60–80 mesh for sleepers, rubber sheets, sealing strips and more.
6. How is steel and nylon fiber separated from the rubber?
Steel wire rings are removed by the SL-1200 debeader. Shredding and crushing help free fibers; mechanical separation, screening and magnetic separators (often used in plants) then separate steel and some fibers. Nylon may also be separated during screening and air classification; additional equipment can be added for enhanced separation.
7. What are the electrical power requirements for the main units?
Power ratings listed: SL-1200: 15 kW; ZPS-1200: 90 kW; PSJ-900: 58 kW; CSJ-600/800: 30 / 37 kW; CXFJ-28: 30.2 kW. Total power depends on the full configuration and concurrent operation.
8. What size tires can this line handle?
Machines specify an outer diameter up to 1200 mm (SL-1200 and ZPS-1200). Larger tires require pre-cutting or a customized solution.
9. Is the plant environmentally friendly and energy efficient?
Yes. The design emphasizes recycling waste tires to useful rubber powder, reducing landfill and raw material use. Energy-saving features depend on configuration; dust collection and emission controls should be installed to minimize pollution.
10. What site and installation requirements should I plan for?
Prepare level foundations sized to machine dimensions, stable power supply sized for total kW, adequate ventilation/dust collection, material handling (conveyors/feeding), and workspace for maintenance. Exact footprint varies by layout—consult supplier with machine dimensions.
11. What routine maintenance is required?
Regularly inspect and replace wear parts (knives, millstones), check bearings and fasteners, lubricate moving parts, clean dust/dirt from housings and filters, and ensure magnetic separators and screens are functioning. Follow manufacturer schedules for bearings and gearboxes.
12. How do I match upstream shredding capacity to the CXFJ-28 powder mill?
CXFJ-28 powder mill capacity is 40–150 kg/h, while upstream shredders/crushers have higher capacities. The mill is often the bottleneck; scale the number of mills or add buffering/storage and feed controls to match upstream throughput and avoid overloading the mill.
13. Can the machine be customized for different outputs or higher capacity?
Yes. Plants can be customized (additional mills, larger crushers, alternative screening) to achieve different mesh sizes, higher throughput or to process other rubber-containing wastes. Contact the supplier for tailored layouts and equipment upgrades.
14. What safety and dust control measures are recommended?
Install dust collectors, enclosed material transfer, emergency stop systems, proper guarding on moving parts, noise reduction measures, and provide PPE and operator training. Regularly maintain seals and filtration to control airborne dust.
15. Are spare parts and operator training available?
Spare parts for wear items (knives, millstones, bearings) and scheduled maintenance parts are typically available from the manufacturer or dealer. Operator training and installation support are usually offered—confirm scope and terms with the supplier.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories
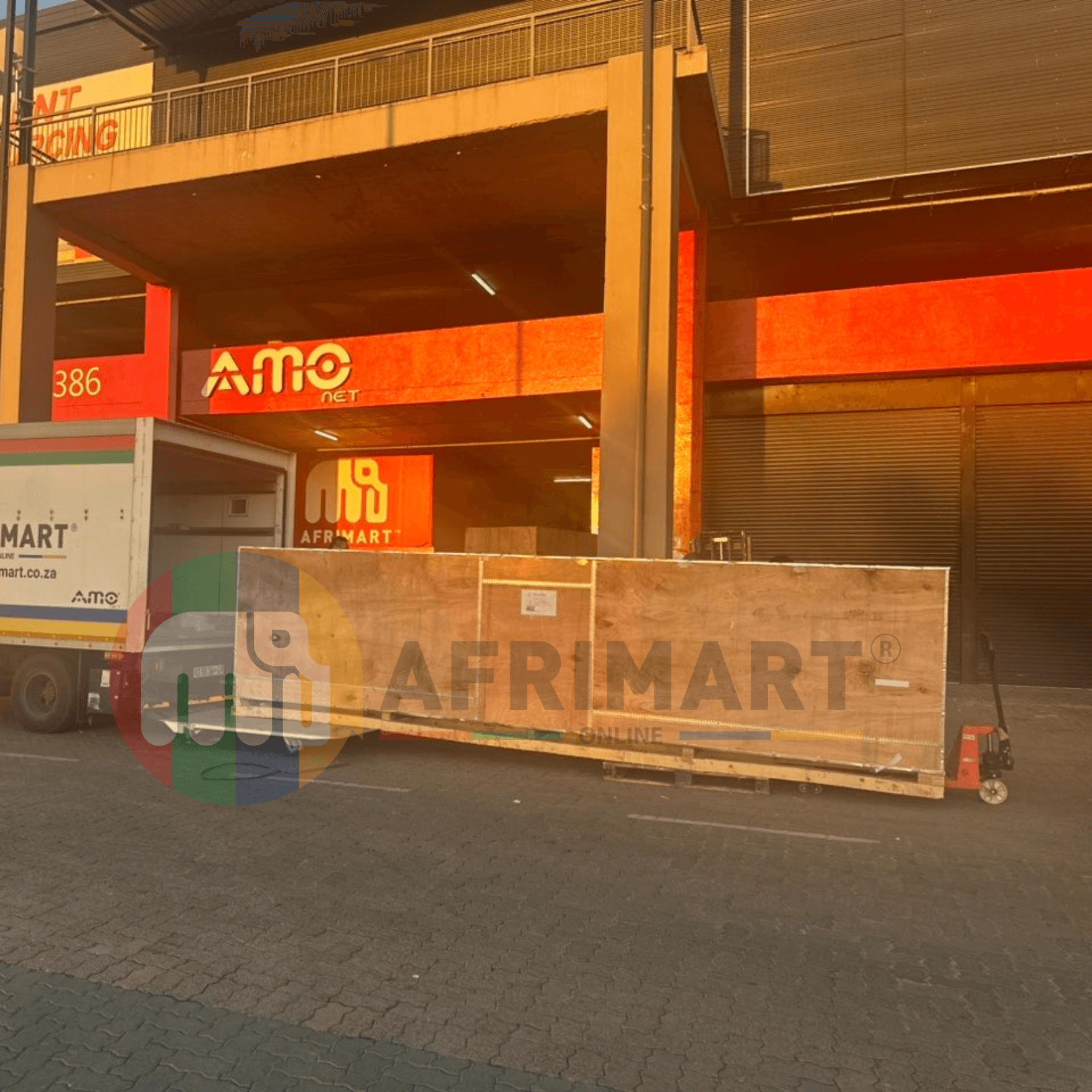

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment
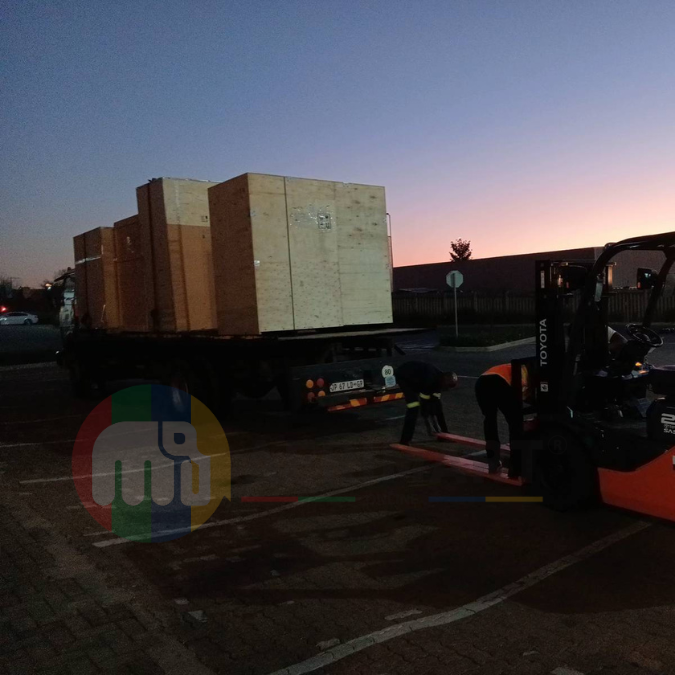

Mining Equipments
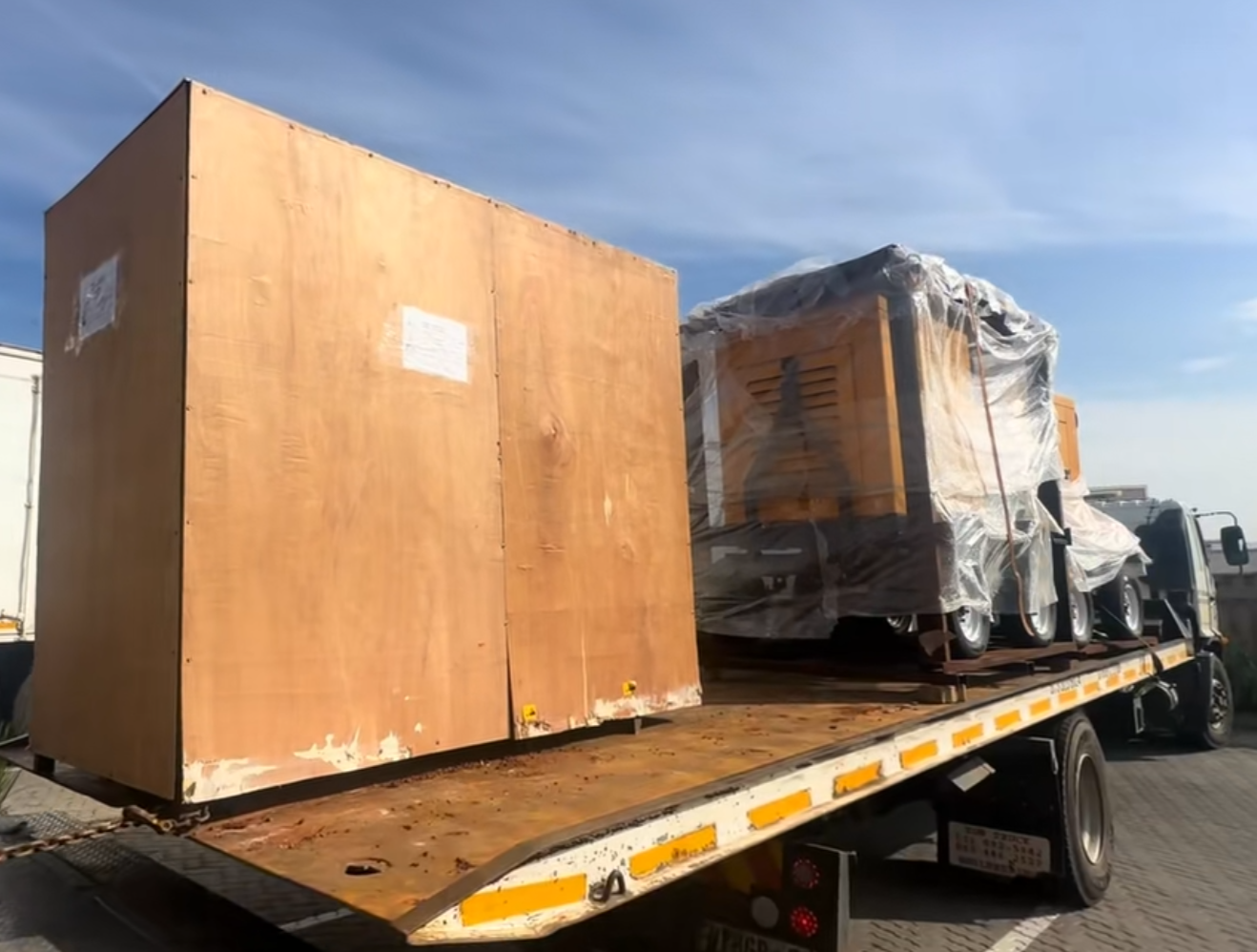

Food Processing Machine
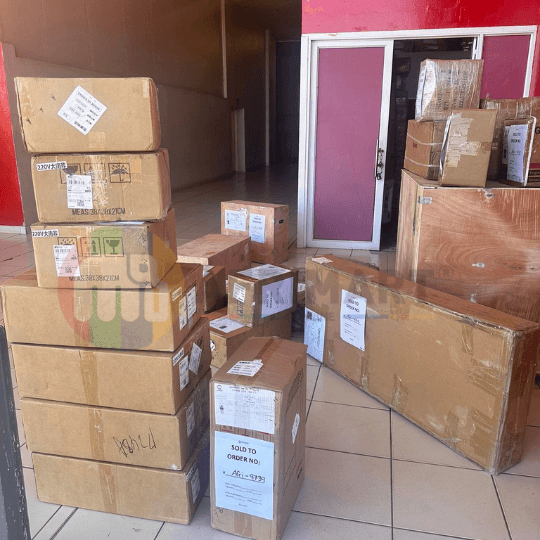

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading
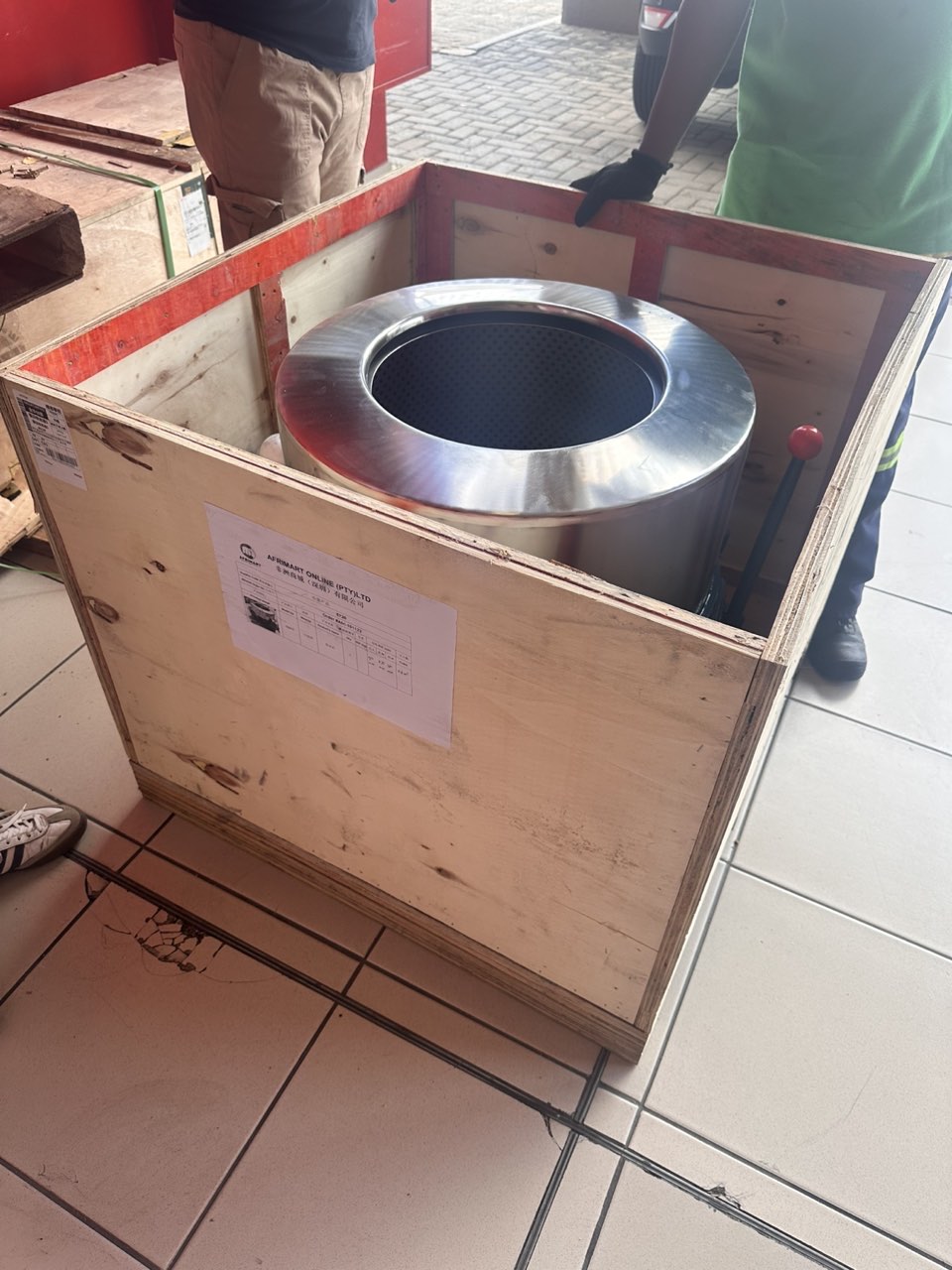

order success

order collection

order offloading





















