B21, China Town Mall, Midrand
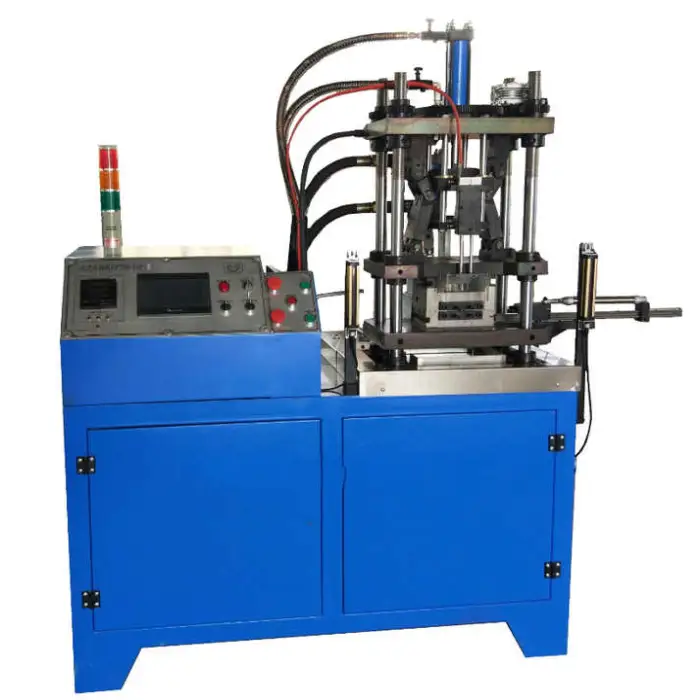
10 Ton Electric Continuous Automatic Vertical Die Casting Machine
- Section : Machinery
- Category : Metal & Metallurgy Machinery
- SKU : 1600206130854

- Shipping Timeframes: All orders are processed within 2-5 business days (excluding weekends and holidays). After your order has been processed, the estimated delivery time is before 23 Apr, 2026, depending on customs, Please note that due to high demand, some items may experience longer shipping times, which will be communicated at order confirmation email.
- Order Processing Time: Please allow 2-5 business days for us to process your order before it is shipped . Orders placed after 16:00 on Fridays, or during weekends and public holidays, will begin processing on the next business day. Processing times may be extended during peak seasons or sales events.
- Manufacturing Time: Some products needs manufacturing time, the manufacturing process will take approximately 10-30 business days depending on the product. This timeframe may vary depending on the complexity of the product and current demand. but this will be communicated with you during order confirmation.
- Returns and Exchanges: We offer a 30-day return policy for most items. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you may return it within 30 days of receipt for a refund or exchange. Items must be unused, in their original packaging, and accompanied by proof of purchase. Return shipping costs are the responsibility of the customer, unless the item was damaged or defective upon arrival.
1. What is the 10 Ton Electric Continuous Automatic Vertical Die Casting Machine used for?
It is a cold-chamber vertical die casting machine designed for high-productivity, precision casting of metal parts such as automotive components, electronic housings, industrial parts and household appliance components.
2. What are the main electrical and power requirements?
Motor voltage is 380 V and rated power is 5.5 kW. A stable three-phase 380 V supply with proper grounding is required. Confirm exact site power and breaker requirements with the supplier before installation.
3. Which alloys and materials can be cast on this cold-chamber machine?
Cold-chamber die casting is typically used for higher-melting-point or more reactive alloys such as aluminum and copper-based alloys. Always confirm alloy compatibility for your specific parts with the manufacturer.
4. What is the machine's maximum casting speed and expected production capacity?
Maximum die casting speed is 10 cycles per minute. Theoretical output at 10/min is 600 parts per hour (4,800 parts per 8-hour shift). The specification lists '1.2–1.6w pcs/day' (commonly interpreted as 12,000–16,000 pcs/day) — actual daily output depends on cycle time, part complexity, number of shifts and uptime.
5. What are the die block thickness limits?
Supported die block thickness ranges from 60 mm (minimum) to 120 mm (maximum). Ensure your mold design falls within this range.
6. What is the maximum lock (clamping) force?
Maximum lock force (clamping force) is 100 kN, which keeps the die closed during injection to prevent flash and ensure part integrity.
7. What are the ejection force and ejection stroke specifications?
Ejection force is 100 kN and ejection stroke is 100 mm. These values determine the ejection capability for part size and weight; validate against your part geometry.
8. What are the machine dimensions and shipping weight?
Machine dimensions are 1450 × 1000 × 1720 mm (L × W × H) and the machine weight is 1000 kg. Allow extra floor space for operator access, tooling and maintenance, and plan for lifting equipment for installation.
9. What does 'continuous automatic' operation mean on this machine?
It indicates automated cycles for mold closing, metal injection, cooling, and ejection to run continuously with minimal manual intervention. Exact automation features (part feeding, conveyors, robot integration) depend on configuration — confirm options with the supplier.
10. What quality assurance and inspection are provided?
The machine includes video outgoing inspection (video-recorded checks of machine operation/parts) and a machinery test report documenting performance and acceptance tests prior to shipment.
11. What are the typical maintenance requirements?
Typical maintenance includes daily visual checks, lubrication, electrical and safety checks, weekly inspection of ejectors and mold alignment, and periodic preventive maintenance per manufacturer schedule. Keep a supply of common wear parts and follow OEM guidance.
12. What site preparation and utilities are required for installation?
Prepare a level, load-bearing foundation or floor area with sufficient clearance, three-phase 380 V power with proper grounding, and space for handling equipment. Many installations also require compressed air and cooling water—confirm exact utilities with the supplier.
13. What safety features should operators expect, and what PPE is required?
Expect emergency stop, safety interlocks/guards and electrical protections. Operators should wear appropriate PPE (safety glasses, heat-resistant gloves, protective clothing and hearing protection). Review the machine's safety documentation and supplier recommendations.
14. Does the supplier provide training and after-sales service?
Most suppliers offer operator and maintenance training, commissioning support and technical documentation. After-sales service availability and warranty terms vary — confirm training, response times and spare-parts support with the vendor.
15. What spare parts and consumables should I keep on hand?
Common spare/consumable items include ejector pins, nozzles, thermocouples, seals, filters and sensors. Discuss a recommended spare-parts list with the supplier based on your production volume and part designs.
Latest Order Arrivals
Discover our latest orders
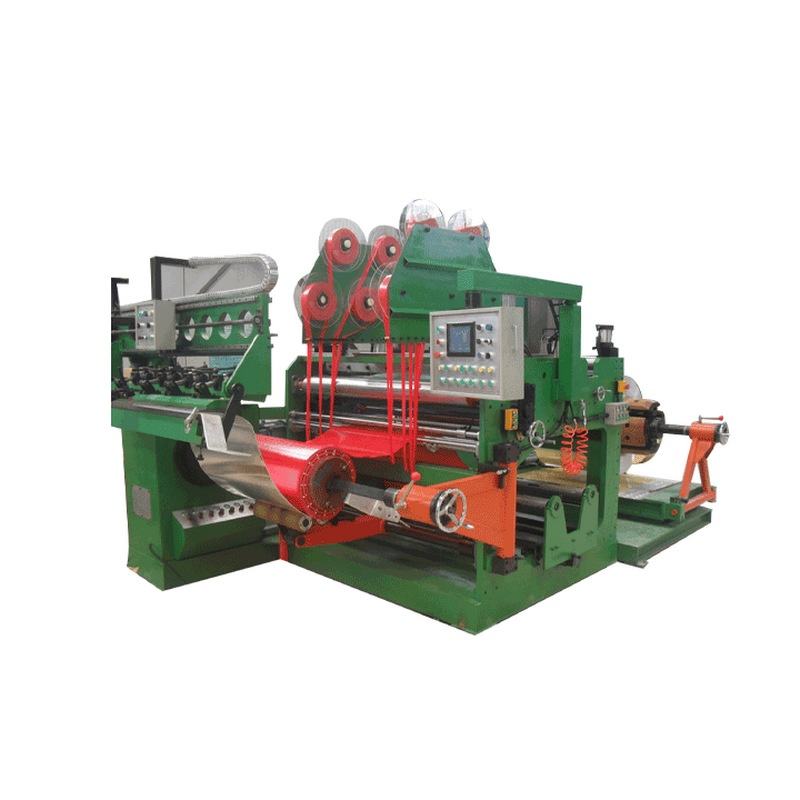
12 Heads Embroidery Machine

Dewatering Pump Machine

Order Collection

Portable Water Drilling Rig

Order Usefully Collected

Batch of Orders

Agriculture Processing Machines

Meat Grinder Machine

Water Pump Equipment

Packaging Machine and accessories

Fabrics Manufacturing Equipment

Mining Equipments

Food Processing Machine

Batch of Orders

Batch of Orders

Latest Orders Labelled
wheel alignment machines

new arrivals
Pre Orders Offloading

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

Latest Arrivals

26 January 2026

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper making machine

Toilet paper Rewinding Machine

latest arrivals

offloading

order success

order collection

order offloading



















